circMbl functions in cis and in trans to regulate gene expression and physiology in a tissue-specific fashion
- PMID: 35476987
- PMCID: PMC9352392
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2022.110740
circMbl functions in cis and in trans to regulate gene expression and physiology in a tissue-specific fashion
Abstract
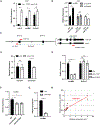
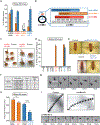
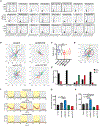
Muscleblind (mbl) is an essential muscle and neuronal splicing regulator. Mbl hosts multiple circular RNAs (circRNAs), including circMbl, which is conserved from flies to humans. Here, we show that mbl-derived circRNAs are key regulators of MBL by cis- and trans-acting mechanisms. By generating fly lines to specifically modulate the levels of all mbl RNA isoforms, including circMbl, we demonstrate that the two major mbl protein isoforms, MBL-O/P and MBL-C, buffer their own levels by producing different types of circRNA isoforms in the eye and fly brain, respectively. Moreover, we show that circMbl has unique functions in trans, as knockdown of circMbl results in specific morphological and physiological phenotypes. In addition, depletion of MBL-C or circMbl results in opposite behavioral phenotypes, showing that they also regulate each other in trans. Together, our results illuminate key aspects of mbl regulation and uncover cis and trans functions of circMbl in vivo.
Keywords: CP: Molecular biology; Drosophila; MBNL; RNA metabolism; circMbl; circRNA; muscleblind; splicing.
Copyright © 2022 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Alexa A, and Rahnenfuhrer J (2021). topGO: Enrichment analysis for Gene Ontology. R package version 2.10.0.
-
- Artero R, Prokop A, Paricio N, Begemann G, Pueyo I, Mlodzik M, Perez-Alonso M, and Baylies MK (1998). The muscleblind gene participates in the organization of Z-bands and epidermal attachments of Drosophila muscles and is regulated by Dmef2. Dev. Biol 195, 131–143. 10.1006/dbio.1997.8833. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

