RNAi-based modulation of IFN-γ signaling in skin
- PMID: 35477658
- PMCID: PMC9372319
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2022.04.019
RNAi-based modulation of IFN-γ signaling in skin
Abstract
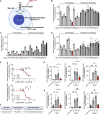
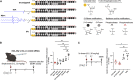
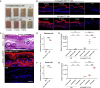
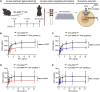
Aberrant activation of interferon (IFN)-γ signaling plays a key role in several autoimmune skin diseases, including lupus erythematosus, alopecia areata, vitiligo, and lichen planus. Here, we identify fully chemically modified small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) that silence the ligand binding chain of the IFN-γ receptor (IFNGR1), for the modulation of IFN-γ signaling. Conjugating these siRNAs to docosanoic acid (DCA) enables productive delivery to all major skin cell types local to the injection site, with a single dose of injection supporting effective IFNGR1 protein reduction for at least 1 month in mice. In an ex vivo model of IFN-γ signaling, DCA-siRNA efficiently inhibits the induction of IFN-γ-inducible chemokines, CXCL9 and CXCL10, in skin biopsies from the injection site. Our data demonstrate that DCA-siRNAs can be engineered for functional gene silencing in skin and establish a path toward siRNA treatment of autoimmune skin diseases.
Keywords: CXCL9/10/11 chemokines; IFN-γ signaling; RNAi therapeutics; autoimmune disorders; immunomodulatory drugs; preclinical drug development; siRNA delivery; skin immunology.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests A.K., J.E.H., and Q.T. have filed a patent that covers the abovementioned IFNGR1 and other (JAK1, JAK2, and STAT1) identified siRNA oligonucleotides for the modulation of IFN-γ signaling pathway. A.K. discloses ownership of stock in RXi Pharmaceuticals and Advirna and is a founder of Atalanta Therapeutics. J.E.H holds equity in Rheos Medicines, TeVido BioDevices and is a founder of Villaris Therapeutics, Aldena Therapeutics, NIRA Biosciences, and Vimela Therapeutics.
Figures

References
-
- Harris J.E., Harris T.H., Weninger W., John Wherry E., Hunter C.A., Turka L.A. A mouse model of vitiligo with focused epidermal depigmentation requires IFN-γ for autoreactive CD8+ T-cell accumulation in the skin. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2012;132:1869–1876. doi: 10.1038/jid.2011.463. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Shao S., Tsoi L.C., Sarkar M.K., Xing X., Xue K., Uppala R., Berthier C.C., Zeng C., Patrick M., Billi A.C., et al. IFN-γ enhances cell-mediated cytotoxicity against keratinocytes via JAK2/STAT1 in lichen planus. Sci. Transl. Med. 2019;11:eaav7561. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aav7561. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Rashighi M., Agarwal P., Richmond J.M., Harris T.H., Dresser K., Su M.-W., Zhou Y., Deng A., Hunter C.A., Luster A.D., et al. CXCL10 is critical for the progression and maintenance of depigmentation in a mouse model of vitiligo. Sci. Transl. Med. 2014;6:223ra23. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3007811. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

