β-Hydroxybutyrate suppresses colorectal cancer
- PMID: 35477756
- PMCID: PMC9448510
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-022-04649-6
β-Hydroxybutyrate suppresses colorectal cancer
Abstract
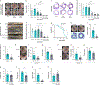
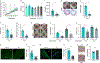
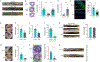
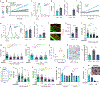
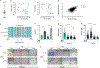
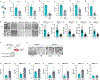
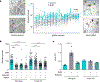
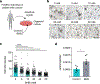
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is among the most frequent forms of cancer, and new strategies for its prevention and therapy are urgently needed1. Here we identify a metabolite signalling pathway that provides actionable insights towards this goal. We perform a dietary screen in autochthonous animal models of CRC and find that ketogenic diets exhibit a strong tumour-inhibitory effect. These properties of ketogenic diets are recapitulated by the ketone body β-hydroxybutyrate (BHB), which reduces the proliferation of colonic crypt cells and potently suppresses intestinal tumour growth. We find that BHB acts through the surface receptor Hcar2 and induces the transcriptional regulator Hopx, thereby altering gene expression and inhibiting cell proliferation. Cancer organoid assays and single-cell RNA sequencing of biopsies from patients with CRC provide evidence that elevated BHB levels and active HOPX are associated with reduced intestinal epithelial proliferation in humans. This study thus identifies a BHB-triggered pathway regulating intestinal tumorigenesis and indicates that oral or systemic interventions with a single metabolite may complement current prevention and treatment strategies for CRC.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


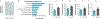



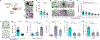
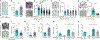
Comment in
-
CRC inhibited by the ketone body β-hydroxybutyrate.Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022 Jul;19(7):416. doi: 10.1038/s41575-022-00636-4. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022. PMID: 35618920 No abstract available.
-
Ketogenic Diet as a Chemopreventative and Therapeutic Strategy for Colon Cancer.Gastroenterology. 2022 Sep;163(3):776-777. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2022.06.046. Epub 2022 Jun 18. Gastroenterology. 2022. PMID: 35728685 No abstract available.
-
Ketogenic diet: new avenues to overcome colorectal cancer.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022 Aug 2;7(1):262. doi: 10.1038/s41392-022-01113-9. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022. PMID: 35918319 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R35 CA263922/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK050306/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK124369/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DP2 AG067511/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 ES013508/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL139783/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA045508/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA218133/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- DP2 AG067492/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AI141393/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AR069589/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA227629/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA168654/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R35 GM138085/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R35 HL140018/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA078831/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AI055400/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA006927/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK019525/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

