Bisdemethoxycurcumin-mediated Attenuation of Apoptosis Prevents Gentamicin-induced Ototoxicity in Mouse Cochlear UB/OC-2 Cells
- PMID: 35478148
- PMCID: PMC9087079
- DOI: 10.21873/invivo.12807
Bisdemethoxycurcumin-mediated Attenuation of Apoptosis Prevents Gentamicin-induced Ototoxicity in Mouse Cochlear UB/OC-2 Cells
Abstract
Background/aim: Gentamicin has been widely prescribed since the last two decades despite its ototoxicity and nephrotoxicity. Bisdemethoxycurcumin (BDMC) is an affordable and safe curcuminoid with medicinal properties. We aimed to understand the effects of BDMC on the gentamicin-induced hair cell damage in mouse cochlear UB/OC-2 cells, in order to elucidate the therapeutic potential of BDMC against gentamicin-induced ototoxicity.
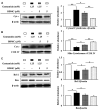
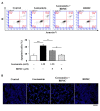
Materials and methods: We quantified the cell membrane potential and examined the regulators and cascade proteins in the intrinsic pathway of hair cell apoptosis. Mouse cochlear UB/OC-2 cells were treated with BDMC before exposure to gentamicin. The effects of BDMC on hair cell viability, mitochondrial function, and apoptosis-related proteins were examined by flow cytometry, western blot, and fluorescent staining.
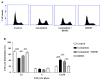
Results: Our results revealed that BDMC reversed gentamicin-mediated cycle arrest at the G2/M phase, stabilizing the mitochondrial membrane potential, decreasing cleaved caspase proteins, and successfully reversing hair cell apoptosis.
Conclusion: BDMC is a potential agent for reducing gentamicin-induced ototoxicity.
Keywords: Gentamicin; apoptosis; bisdemethoxycurcumin; mitochondrial function; ototoxicity; reactive oxygen species.
Copyright © 2022, International Institute of Anticancer Research (Dr. George J. Delinasios), All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The Authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Ameliorative effect of taxifolin on gentamicin-induced ototoxicity via down-regulation of apoptotic pathways in mouse cochlear UB/OC-2 cells.J Chin Med Assoc. 2022 May 1;85(5):617-626. doi: 10.1097/JCMA.0000000000000708. Epub 2022 May 2. J Chin Med Assoc. 2022. PMID: 35286283
-
Otoprotective Effect of 2,3,4',5-Tetrahydroxystilbene-2-O-β-d-Glucoside on Gentamicin-Induced Apoptosis in Mouse Cochlear UB/OC-2 Cells.Molecules. 2020 Jul 6;25(13):3070. doi: 10.3390/molecules25133070. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32640539 Free PMC article.
-
Otoprotective Effects of Fucoidan Reduce Cisplatin-Induced Ototoxicity in Mouse Cochlear UB/OC-2 Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 10;24(4):3561. doi: 10.3390/ijms24043561. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36834972 Free PMC article.
-
Baicalin attenuates gentamicin-induced cochlear hair cell ototoxicity.J Appl Toxicol. 2019 Aug;39(8):1208-1214. doi: 10.1002/jat.3806. Epub 2019 Apr 25. J Appl Toxicol. 2019. PMID: 31021006
-
Puerarin alleviates the ototoxicity of gentamicin by inhibiting the mitochondria‑dependent apoptosis pathway.Mol Med Rep. 2021 Dec;24(6):851. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2021.12491. Epub 2021 Oct 15. Mol Med Rep. 2021. PMID: 34651662 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Therapeutic potential of salidroside in preserving rat cochlea organ of corti from gentamicin-induced injury through modulation of NRF2 signaling and GSK3β/NF-κB pathway.PLoS One. 2024 Mar 14;19(3):e0298529. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0298529. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38483863 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
