Metastatic Urinary Bladder Carcinoma on Palliative Chemotherapy Showing Rapid Progression on Interim Fluorodeoxyglucose Positron Emission Tomography/Computed Tomography
- PMID: 35478686
- PMCID: PMC9037868
- DOI: 10.4103/ijnm.ijnm_51_21
Metastatic Urinary Bladder Carcinoma on Palliative Chemotherapy Showing Rapid Progression on Interim Fluorodeoxyglucose Positron Emission Tomography/Computed Tomography
Abstract
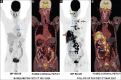
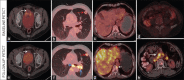
Bladder cancer (BC) is among the top ten most common cancer types globally. Muscle invasive BC has a high incidence of metastasis. Metastatic BC has a poor prognosis and limited treatment options. Here, we present a middle-aged man with oligometastatic BC, which was treated with palliative chemotherapy. He had significant clinical improvement. However, interim 18F-Fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography demonstrates a rapid disease progression extensive metastasis.
Keywords: Fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography; metastatic disease; progressive disease; treatment response evaluation; urinary bladder carcinoma.
Copyright: © 2022 Indian Journal of Nuclear Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Višnjar T, Romih R, Zupančič D. Lectins as possible tools for improved urinary bladder cancer management. Glycobiology. 2019;29:355–65. - PubMed
-
- Antoni S, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Znaor A, Jemal A, Bray F. Bladder cancer incidence and mortality: A global overview and recent trends. Eur Urol. 2017;71:96–108. - PubMed
-
- Burger M, Catto JW, Dalbagni G, Grossman HB, Herr H, Karakiewicz P, et al. Epidemiology and risk factors of urothelial bladder cancer. Eur Urol. 2013;63:234–41. - PubMed
-
- Shinagare AB, Ramaiya NH, Jagannathan JP, Fennessy FM, Taplin ME, Van den Abbeele AD. Metastatic pattern of bladder cancer: Correlation with the characteristics of the primary tumor. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2011;196:117–22. - PubMed
-
- Nadal R, Bellmunt J. Management of metastatic bladder cancer. Cancer Treat Rev. 2019;76:10–21. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
