Enzyme cascade-amplified immunoassay based on the nanobody-alkaline phosphatase fusion and MnO2 nanosheets for the detection of ochratoxin A in coffee
- PMID: 35478809
- PMCID: PMC9034093
- DOI: 10.1039/d1ra03615g
Enzyme cascade-amplified immunoassay based on the nanobody-alkaline phosphatase fusion and MnO2 nanosheets for the detection of ochratoxin A in coffee
Abstract
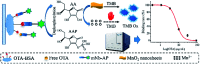
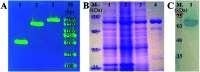
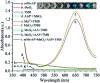
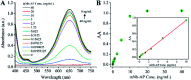
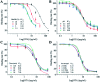
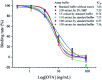
Ochratoxin A (OTA) is a common food contaminant with multiple toxicities and thus rapid and accurate detection of OTA is indispensable to minimize the threat of OTA to public health. Herein a novel enzyme cascade-amplified immunoassay (ECAIA) based on the mutated nanobody-alkaline phosphatase fusion (mNb-AP) and MnO2 nanosheets was established for detecting OTA in coffee. The detection principle is that the dual functional mNb-AP could specifically recognize OTA and dephosphorylate the ascorbic acid-2-phosphate (AAP) into ascorbic acid (AA), and the MnO2 nanosheets mimicking the oxidase could be reduced by AA into Mn2+ and catalyze the 3,3',5,5'-tetramethyl benzidine into blue oxidized product for quantification. Using the optimal conditions, the ECAIA could be finished within 132.5 min and shows a limit of detection of 3.38 ng mL-1 (IC10) with an IC50 of 7.65 ng mL-1 and a linear range (IC20-IC80) of 4.55-12.85 ng mL-1. The ECAIA is highly selective for OTA. Good recovery rates (84.3-113%) with a relative standard deviation of 1.3-3% were obtained and confirmed by high performance liquid chromatography with a fluorescence detector. The developed ECAIA was demonstrated to be a useful tool for the detection of OTA in coffee which provides a reference for the analysis of other toxic small molecules.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Amézqueta S. Schorr-Galindo S. Murillo-Arbizu M. González-Peñas E. López de Cerain A. Guiraud J. P. Food Control. 2012;26:259–268. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2012.01.042. - DOI
-
- International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC), 1993
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

