Solvent-free synthesis of propargylamines: an overview
- PMID: 35479216
- PMCID: PMC9033675
- DOI: 10.1039/d1ra03324g
Solvent-free synthesis of propargylamines: an overview
Abstract
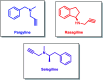
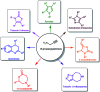
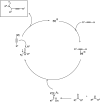
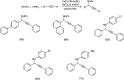
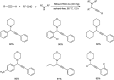
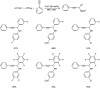
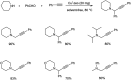
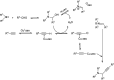
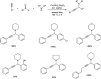
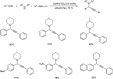
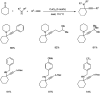
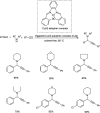
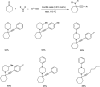
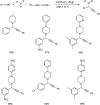
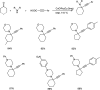
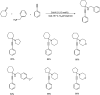
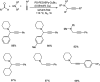
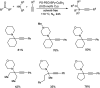
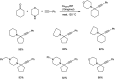
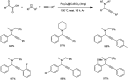
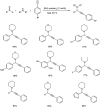
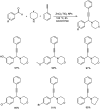
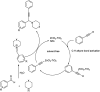
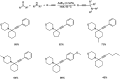
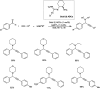
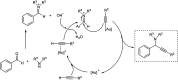
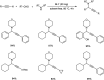
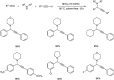
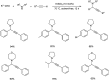
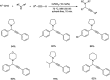
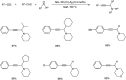
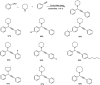
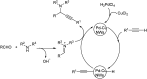
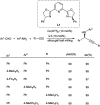
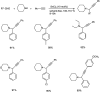
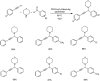
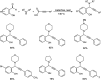
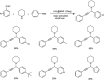
Propargylamines are a class of compounds with many pharmaceutical and biological properties. A green approach to synthesize such compounds is very relevant. This review aims to describe the solvent-free synthetic approaches towards propargylamines via A3 and KA2 coupling reactions covering the literature up to 2021.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures
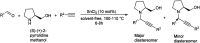



Similar articles
-
Synthesis and Reactivity of Propargylamines in Organic Chemistry.Chem Rev. 2017 Dec 27;117(24):14091-14200. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.7b00343. Epub 2017 Nov 22. Chem Rev. 2017. PMID: 29166000
-
α-Tertiary Propargylamine Synthesis via KA2-Type Coupling Reactions under Solvent-Free CuI-Zeolite Catalysis.J Org Chem. 2021 Dec 3;86(23):16593-16613. doi: 10.1021/acs.joc.1c01893. Epub 2021 Nov 21. J Org Chem. 2021. PMID: 34806367
-
Metal-free multicomponent approach for the synthesis of propargylamine: a review.RSC Adv. 2021 Jan 7;11(4):2047-2065. doi: 10.1039/d0ra09392k. eCollection 2021 Jan 6. RSC Adv. 2021. PMID: 35424169 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Enantioselective decarboxylative Mannich reaction of β-keto acids with C-alkynyl N-Boc N,O-acetals: access to chiral β-keto propargylamines.Org Biomol Chem. 2021 Oct 14;19(39):8607-8612. doi: 10.1039/d1ob01555a. Org Biomol Chem. 2021. PMID: 34569587
-
Solvent-free incorporation of CO2 into 2-oxazolidinones: a review.RSC Adv. 2019 Jun 21;9(34):19465-19482. doi: 10.1039/c9ra00551j. eCollection 2019 Jun 19. RSC Adv. 2019. PMID: 35519371 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Gold nanoparticle decorated dithiocarbamate modified natural boehmite as a catalyst for the synthesis of biologically essential propargylamines.RSC Adv. 2022 Nov 7;12(49):31680-31687. doi: 10.1039/d2ra03725d. eCollection 2022 Nov 3. RSC Adv. 2022. PMID: 36380962 Free PMC article.
-
Silver and Gold Complexes with NHC-Ligands Derived from Caffeine: Catalytic and Pharmacological Activity.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Feb 23;25(5):2599. doi: 10.3390/ijms25052599. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38473851 Free PMC article.
-
Application of magnetic deep eutectic solvents as an efficient catalyst in the synthesis of new 1,2,3-triazole-nicotinonitrile hybrids via a cooperative vinylogous anomeric-based oxidation.RSC Adv. 2024 Oct 29;14(47):34668-34678. doi: 10.1039/d4ra05177g. eCollection 2024 Oct 29. RSC Adv. 2024. PMID: 39479491 Free PMC article.
-
N-Heterocyclic Carbene Silver Complex Modified Polyacrylonitrile Fiber/MIL-101(Cr) Composite as Efficient Chiral Catalyst for Three-Component Coupling Reaction.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022 Nov 24;12(23):4175. doi: 10.3390/nano12234175. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36500798 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

