Recent progress in cadmium fluorescent and colorimetric probes
- PMID: 35479541
- PMCID: PMC9040829
- DOI: 10.1039/d1ra05048f
Recent progress in cadmium fluorescent and colorimetric probes
Abstract
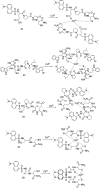
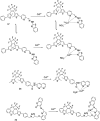
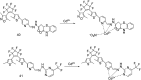
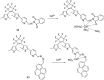
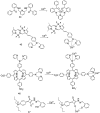
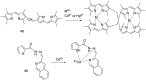
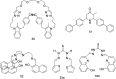
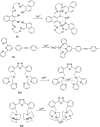
Cadmium is a heavy metal which exists widely in industrial and agricultural production and can induce a variety of diseases in organisms. Therefore, its detection is of great significance in the fields of biology, environment and medicine. Fluorescent probe has been a powerful tool for cadmium detection because of its convenience, sensitivity, and bioimaging capability. In this paper, we reviewed 98 literatures on cadmium fluorescent sensors reported from 2017 to 2021, classified them according to different fluorophores, elaborated the probe design, application characteristics and recognition mode, summarized and prospected the development of cadmium fluorescent and colorimetric probes. We hope to provide some help for researchers to design cadmium fluorescent probes with higher selectivity, sensitivity and practicability.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures




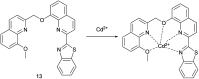
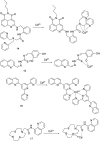


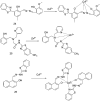

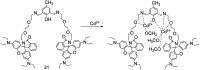










References
-
- Li J. Chen Y. H. Chen T. T. Qiang J. Zhang Z. J. Wei T. W. Zhang W. Wang F. Chen X. Q. Sens. Actuators, B. 2018;268:446–455. doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2018.04.130. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

