Air Pollution and Chronic Kidney Disease Risk in Oil and Gas- Situated Communities: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 35479765
- PMCID: PMC9035494
- DOI: 10.3389/ijph.2022.1604522
Air Pollution and Chronic Kidney Disease Risk in Oil and Gas- Situated Communities: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Objective: This systematic review and meta-analysis aimed at synthesising epidemiological data on the association between long-term air pollution and kidney-related outcomes in oil and natural gas (ONG) situated communities. Methods: We synthesised studies using the PRISMA 2020 guideline. We searched databases including Medline, Cochrane Library, CIHANL, CAB Abstracts, Greenlife, African Journal Online, Google Scholar and Web of Science, from inception to April 2021. Heterogeneity across studies and publication bias were assessed. Results: Twenty-five studies were systematically reviewed but only 14 were included in the meta-analysis and categorised based on the outcome studied. Residents of exposed communities have increased risk for Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) (OR = 1.70, 95% CI 1.44-2.01), lower eGFR (OR = 0.55, 95% CI 0.48-0.67) and higher serum creatinine (OR = 1.39, 95% CI 1.06-1.82) compared to less exposed or unexposed populations. The risks for hypertension and kidney cancer between the two populations were not significantly different. Conclusion: We report an increased risk for CKD and kidney dysfunction in populations residing near petrochemical plants, although from a limited number of studies. The scientific community needs to explore this environment and non-communicable disease relationship, particularly in vulnerable populations.
Keywords: air pollution; hypertension; kidney disease; meta-analysis; oil and natural gas; petrochemical plants; systematic review.
Copyright © 2022 Okoye, Carnegie and Mora.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
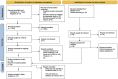




References
-
- Mudu P, Terracini B, Martuzzi M. Human Health in Areas with Industrial Contamination. Copenhagen: WHO Regional Office for Europe; (2014).
-
- World Health Organisation. Ambient (Outdoor)air Pollution. [Factsheet] (2018). Available at: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/ambient-(outdoor)-air-q... (Accessed December 11 2020).
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

