Improved Artificial Neural Network with State Order Dataset Estimation for Brain Cancer Cell Diagnosis
- PMID: 35480141
- PMCID: PMC9038414
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/7799812
Improved Artificial Neural Network with State Order Dataset Estimation for Brain Cancer Cell Diagnosis
Retraction in
-
Retracted: Improved Artificial Neural Network with State Order Dataset Estimation for Brain Cancer Cell Diagnosis.Biomed Res Int. 2023 Dec 29;2023:9842518. doi: 10.1155/2023/9842518. eCollection 2023. Biomed Res Int. 2023. PMID: 38188802 Free PMC article.
Abstract
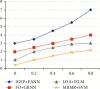
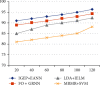
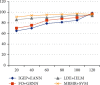
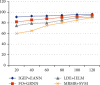
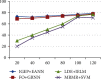
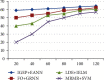
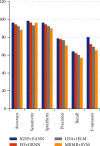
Brain cancer is one of the cell synthesis diseases. Brain cancer cells are analyzed for patient diagnosis. Due to this composite cell, the conceptual classifications differ from each and every brain cancer investigation. In the gene test, patient prognosis is identified based on individual biocell appearance. Classification of advanced artificial neural network subtypes attains improved performance compared to previous enhanced artificial neural network (EANN) biocell subtype investigation. In this research, the proposed features are selected based on improved gene expression programming (IGEP) with modified brute force algorithm. Then, the maximum and minimum term survivals are classified by using PCA with enhanced artificial neural network (EANN). In this, the improved gene expression programming (IGEP) effectual features are selected by using remainder performance to improve the prognosis efficiency. This system is estimated by using the Cancer Genome Atlas (CGA) dataset. Simulation outputs present improved gene expression programming (IGEP) with modified brute force algorithm which achieves accurate efficiency of 96.37%, specificity of 96.37%, sensitivity of 98.37%, precision of 78.78%, F-measure of 80.22%, and recall of 64.29% when compared to generalized regression neural network (GRNN), improved extreme learning machine (IELM) with minimum redundancy maximum relevance (MRMR) method, and support vector machine (SVM).
Copyright © 2022 D. N. V. S. L. S. Indira et al.
Conflict of interest statement
There is no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Cortes C., Gonzalvo X., Kuznetsov V., Mohri M., Yang S. Adanet: adaptive structural learning of artificial neural networks. 2016. http://arxiv.org/abs/1607.01097 .
-
- Elkatatny S., Mahmoud M., Tariq Z., Abdulraheem A. New insights into the prediction of heterogeneous carbonate reservoir permeability from well logs using artificial intelligence network. Neural Computing and Applications . 2018;30(9):2673–2683. doi: 10.1007/s00521-017-2850-x. - DOI
-
- Wang L., Yang B., Wang S., Liang Z. Building image feature kinetics for cement hydration using gene expression programming with similarity weight tournament selection. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation . 2015;19(5):679–693. doi: 10.1109/tevc.2014.2367111. - DOI
-
- Sharma M., Purohit G. N., Mukherjee S. Information retrieves from brain MRI images for tumor detection using hybrid technique K-means and artificial neural network (KMANN). Proceeding of the International Conference on Networking Communication and Data Knowledge Engineering; November 3 2018; Singapore. Springer; pp. 145–157.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

