Novel Indel Variation of NPC1 Gene Associates With Risk of Sudden Cardiac Death
- PMID: 35480314
- PMCID: PMC9035640
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2022.869859
Novel Indel Variation of NPC1 Gene Associates With Risk of Sudden Cardiac Death
Abstract
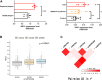
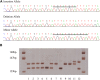
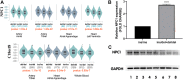
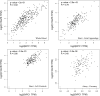
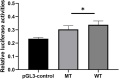
Background and Aims: Sudden cardiac death (SCD) was defined as an unexpected death from cardiac causes during a very short duration. It has been reported that Niemann-Pick type C1 (NPC1) gene mutations might be related to cardiovascular diseases. The purpose of the study is to investigate whether common genetic variants of NPC1 is involved in SCD susceptibility. Methods: Based on a candidate-gene-based approach and systematic screening strategy, this study analyzed an 8-bp insertion/deletion polymorphism (rs150703258) within downstream of NPC1 for the association with SCD risk in Chinese populations using 158 SCD cases and 524 controls. The association of rs150703258 and SCD susceptibility was analyzed using logistic regression. Genotype-phenotype correlation analysis was performed using public database including 1000G, expression quantitative trait loci (eQTL), and further validated by human heart tissues using PCR. Dual-luciferase assay was used to explore the potential regulatory role of rs150703258. Gene expression profiling interactive analysis and transcription factors prediction were performed. Results: Logistic regression analysis exhibited that the deletion allele of rs150703258 significantly increased the risk of SCD [odds ratio (OR) = 1.329; 95% confidence interval (95%CI):1.03-1.72; p = 0.0289]. Genotype-phenotype correlation analysis showed that the risk allele was significantly associated with higher expression of NPC1 at mRNA and protein expressions level in human heart tissues. eQTL analysis showed NPC1 and C18orf8 (an adjacent gene to NPC1) are both related to rs150703258 and have higher expression level in the samples with deletion allele. Dual-luciferase activity assays indicate a significant regulatory role for rs150703258. Gene expression profiling interactive analysis revealed that NPC1 and C18orf8 seemed to be co-regulated in human blood, arteries and heart tissues. In silico analysis showed that the rs150703258 deletion variant may create transcription factor binding sites. In addition, a rare 12-bp allele (4-bp longer than the insertion allele) of rs150703258 was discovered in the current cohort. Conclusion: In summary, our study revealed that rs150703258 might contribute to SCD susceptibility by regulating NPC1 and C18orf8 expression. This indel may be a potential marker for risk stratification and molecular diagnosis of SCD. Validations in different ethnic groups with larger sample size and mechanism explorations are warranted to confirm our findings.
Keywords: NPC1; genetic susceptibility; indel polymorphism; rs150703258; sudden cardiac death.
Copyright © 2022 Zhao, Zhang, Wang, Yu, Zhen, Li, Qu, He, Zhang, Li, Zhang, Luo, Huang and Gao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Novel indel variation of LTBP4 gene associates with risk of sudden cardiac death in Chinese populations with coronary artery disease.Leg Med (Tokyo). 2024 Jul;69:102437. doi: 10.1016/j.legalmed.2024.102437. Epub 2024 Mar 23. Leg Med (Tokyo). 2024. PMID: 38547642
-
Regulatory variation within 3'UTR of STAT5A correlates with sudden cardiac death in Chinese populations.Forensic Sci Res. 2021 Jul 23;7(4):726-735. doi: 10.1080/20961790.2021.1895410. eCollection 2022. Forensic Sci Res. 2021. PMID: 37101540 Free PMC article.
-
TBX5 genetic variants and SCD-CAD susceptibility: insights from Chinese Han cohorts.PeerJ. 2024 Mar 19;12:e17139. doi: 10.7717/peerj.17139. eCollection 2024. PeerJ. 2024. PMID: 38525280 Free PMC article.
-
Association between an indel polymorphism in the 3'UTR of COL1A2 and the risk of sudden cardiac death in Chinese populations.Leg Med (Tokyo). 2017 Sep;28:22-26. doi: 10.1016/j.legalmed.2017.07.006. Epub 2017 Jul 19. Leg Med (Tokyo). 2017. PMID: 28738217
-
Sudden cardiac death: a nationwide cohort study among the young.Dan Med J. 2016 Dec;63(12):B5321. Dan Med J. 2016. PMID: 27910804 Review.
Cited by
-
Glycosphingolipids in Cardiovascular Disease: Insights from Molecular Mechanisms and Heart Failure Models.Biomolecules. 2024 Oct 8;14(10):1265. doi: 10.3390/biom14101265. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39456198 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Differential gene expression patterns in Niemann-Pick Type C and Tay-Sachs diseases: Implications for neurodegenerative mechanisms.PLoS One. 2025 Mar 19;20(3):e0319401. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0319401. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40106490 Free PMC article.
-
The health impacts and genetic architecture of food liking in cardio-metabolic diseases.Nat Commun. 2025 May 23;16(1):4810. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-59945-2. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40410146 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

