Subtle morpho-functional kidney changes in type-2 diabetes mellitus patients: A duplex ultrasound assessment
- PMID: 35480526
- PMCID: PMC9002409
- DOI: 10.12669/pjms.38.3.4699
Subtle morpho-functional kidney changes in type-2 diabetes mellitus patients: A duplex ultrasound assessment
Abstract
Objectives: Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a common endocrine disease with serious effects on multiple organs including the kidneys. This study aimed to investigate the subtle effects of type 2 DM (T2DM) on the kidneys.
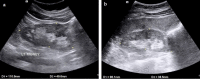
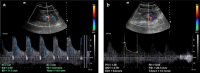
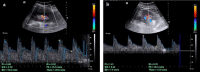
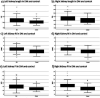
Methods: This was a prospective case-control study conducted in the Radiology Department of University of Science and Technology Hospital (USTH) campus, Sana'a, Republic of Yemen, from 1 January 2020 to 31 November 2020. The renal length (RL), renal width (RW), resistive index (RI), and pulsatility index (PI) were prospectively measured in patients with T2DM and healthy controls. The results were compared using the independent samples t-test. Comparisons were likewise performed between patients with controlled DM and patients with uncontrolled DM.
Results: A total of hundred individuals, 50 diabetic patients and 50 controls, were enrolled in this study. Their mean age was 54 ± 7.88 years (range: 40-75 years). The RL, RI, and PI of both kidneys were significantly higher in T2DM than in the control group. Moreover, the RL, RI, PI and creatinine were slightly higher in patients with uncontrolled than in those with controlled DM.
Conclusion: T2DM has significant accentuating effects on the RL, RI and PI associated with low effective renal plasma flow, even before acute kidney injury or chronic kidney disease diagnosis, which may be attenuated by careful regulation of DM. Ultrasound Doppler is a highly valuable imaging modality for evaluating the subtle effects of T2DM on kidney dimensions and blood flow. The RI can be implemented as a tool for the early diagnosis of kidney disease and contribute to slowing the disease progression and preventing renal failure.
Keywords: Doppler dynamic measurements; Pulsatility index; Renal length; Renal resistive index; Subtle kidney changes.
Copyright: © Pakistan Journal of Medical Sciences.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: None.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Resistive Index of Intrarenal Artery in Evaluation of Diabetic Nephropathy.Bangladesh Med Res Counc Bull. 2015 Dec;41(3):125-130. doi: 10.3329/bmrcb.v41i3.29888. Bangladesh Med Res Counc Bull. 2015. PMID: 29870167
-
The pulsatility index and the resistive index in renal arteries in patients with hypertension and chronic renal failure.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 1995 Nov;10(11):2060-4. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 1995. PMID: 8643168
-
Comparison of Supersonic Shear Wave Imaging-Derived Renal Parenchyma Stiffness Between Diabetes Mellitus Patients With and Without Diabetic Kidney Disease.Ultrasound Med Biol. 2020 Jul;46(7):1630-1640. doi: 10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2020.03.026. Epub 2020 May 11. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2020. PMID: 32404297
-
Influence of proteinuria on renal Doppler sonographic measurements in chronic kidney disease and in diabetes mellitus.J Clin Ultrasound. 2011 Nov-Dec;39(9):506-11. doi: 10.1002/jcu.20822. Epub 2011 May 6. J Clin Ultrasound. 2011. PMID: 21557251
-
The renal resistive index as a new complementary tool to predict microvascular diabetic complications in children and adolescents: a groundbreaking finding.Ann Transl Med. 2019 Sep;7(17):422. doi: 10.21037/atm.2019.08.65. Ann Transl Med. 2019. PMID: 31660321 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Investigation Study of Ultrasound Practitioners' Awareness about Artefacts of Hepatobiliary Imaging in Almadinah Almunawwarah.Pak J Med Sci. 2022 Jul-Aug;38(6):1526-1533. doi: 10.12669/pjms.38.6.5084. Pak J Med Sci. 2022. PMID: 35991221 Free PMC article.
-
Accuracy of Transverse Cerebellar Diameter in Estimating Gestational Age in the Second and Third Trimester: A Prospective Study in Saudi Arabia.Diagnostics (Basel). 2025 Apr 29;15(9):1130. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics15091130. Diagnostics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40361948 Free PMC article.
-
Investigating the Accuracy of Ultrasound Imaging in Measuring Fetal Weight in Comparison with the Actual Postpartum Weight.Pediatr Rep. 2025 Jun 24;17(4):70. doi: 10.3390/pediatric17040070. Pediatr Rep. 2025. PMID: 40700058 Free PMC article.
-
Applicability of creatinine-based glomerular filtration rate assessment equations to patients with neurogenic bladder.Front Physiol. 2024 Dec 9;15:1501161. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2024.1501161. eCollection 2024. Front Physiol. 2024. PMID: 39720311 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association Between Nephrolith Size and Location and Grade of Hydronephrosis.Life (Basel). 2025 Feb 19;15(2):321. doi: 10.3390/life15020321. Life (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40003729 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rodriguez-de-Velasquez A, Yoder IC, Velasquez PA, Papanicolaou N. Imaging the effects of diabetes on the genitourinary system. Radiographics. 1995;15(5):1051–1068. doi:10.1148/radiographics.15.5.7501850. - PubMed
-
- O'Neill WC. Sonographic evaluation of renal failure. Am J Kidney Dis. 2000;35(6):1021–38. doi:10.1016/s0272-6386(00)70036-9. - PubMed
-
- Ablett MJ, Coulthard A, Lee RE, Richardson DL, Bellas T, Owen JP, Keir MJ, Butler TJ. How reliable are ultrasound measurements of renal length in adults? Br J Radiol. 1995;68(814):1087–1089. doi:10.1259/0007-1285-68-814-1087. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
