Low-cost potentiometric paper-based analytical device based on newly synthesized macrocyclic pyrido-pentapeptide derivatives as novel ionophores for point-of-care copper(ii) determination
- PMID: 35480650
- PMCID: PMC9037668
- DOI: 10.1039/d1ra04712d
Low-cost potentiometric paper-based analytical device based on newly synthesized macrocyclic pyrido-pentapeptide derivatives as novel ionophores for point-of-care copper(ii) determination
Abstract
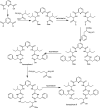
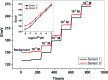
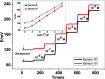
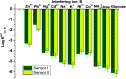
A simple, cost-effective, portable and disposable paper-based analytical device is designed and fabricated for copper(ii) determination. All solid-state ion-selective electrodes (ISEs) for copper and a Ag/AgCl reference electrode were constructed and optimized on the paper substrate. The copper electrodes were built using carbon nano-tube ink as a conductive substrate and an ion-to electron transducer. A suitable polymeric membrane is drop-cast on the surface of the conductive carbon ink window. The copper-sensing membrane is based on newly synthesized macrocyclic pyrido-pentapeptide derivatives as novel ionophores for copper detection. Under the optimized conditions, the presented all-solid-state paper-based Cu2+-ISEs showed a Nernstian response toward Cu2+ ions in 30 mM MES buffer, pH 7.0 over the linear range of 5.0 × 10-7-1.0 × 10-3 M with a limit of detection of 8.0 × 10-8 M. The copper-based sensors exhibited rapid detection of Cu2+ ions with a short response time (<10 s). The selectivity pattern of these new ionophores towards Cu2+ ions over many common mono-, di- and trivalent cations was evaluated using the modified separate solution method (MSSM). The presented paper-based analytical device exhibited good intra-day and inter day precision. The presented tool was successfully applied for trace Cu2+ detection in real samples of serum and whole blood collected from different children with autism spectrum disorder. The data obtained by the proposed potentiometric method were compared with those obtained by the inductively-coupled plasma (ICP) as a reference method. The presented copper paper-based analytical-device can be considered as an attractive tool for point-of-care copper determination because of its affordability, vast availability, and self-pumping ability, particularly when combined with potentiometric detection.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Paper-Based Analytical Device Based on Potentiometric Transduction for Sensitive Determination of Phenobarbital.ACS Omega. 2023 Nov 8;8(46):43538-43545. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c03977. eCollection 2023 Nov 21. ACS Omega. 2023. PMID: 38027332 Free PMC article.
-
Single-Piece Solid Contact Cu2+-Selective Electrodes Based on a Synthesized Macrocyclic Calix[4]arene Derivative as a Neutral Carrier Ionophore.Molecules. 2019 Mar 6;24(5):920. doi: 10.3390/molecules24050920. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 30845715 Free PMC article.
-
Development of Chromium(III) Selective Potentiometric Sensors for Its Determination in Petroleum Water Samples Using Synthesized Nano Schiff Base Complex as an Ionophore.J AOAC Int. 2022 Apr 27;105(3):727-738. doi: 10.1093/jaoacint/qsab166. J AOAC Int. 2022. PMID: 34935954
-
New Potentiometric Screen-Printed Platforms Modified with Reduced Graphene Oxide and Based on Man-Made Imprinted Receptors for Caffeine Assessment.Polymers (Basel). 2022 May 10;14(10):1942. doi: 10.3390/polym14101942. Polymers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35631825 Free PMC article.
-
Non-enzymatic paper-based analytical device for direct potentiometric detection of urine creatinine.Mikrochim Acta. 2024 Feb 9;191(3):128. doi: 10.1007/s00604-024-06203-9. Mikrochim Acta. 2024. PMID: 38334814
Cited by
-
A Novel Calix[4]Crown-Based 1,3,4-Oxadiazole as a Fluorescent Chemosensor for Copper(II) Ion Detection.Front Chem. 2021 Nov 12;9:766442. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2021.766442. eCollection 2021. Front Chem. 2021. PMID: 34869207 Free PMC article.
-
Advancements in electrochemical sensingTechnology for Heavy Metal Ions Detection.Food Chem X. 2025 Jan 20;25:102204. doi: 10.1016/j.fochx.2025.102204. eCollection 2025 Jan. Food Chem X. 2025. PMID: 39911752 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

