Synthesis, Characterization, and In V ivo Toxicological Evaluation of Copper (II) Oxide Containing Herbometallic Siddha Nanocomplex "Thamira Parpam"
- PMID: 35480968
- PMCID: PMC9037038
- DOI: 10.3389/fbioe.2022.849441
Synthesis, Characterization, and In V ivo Toxicological Evaluation of Copper (II) Oxide Containing Herbometallic Siddha Nanocomplex "Thamira Parpam"
Abstract
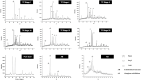
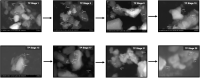
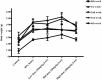
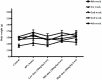
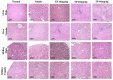
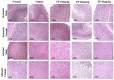
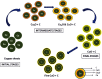
"Thamira parpam" (TP), a copper-based herbometallic oxide (copper (II) oxide) nanodrug has been used in Siddha medicine for centuries because of its anti-ulcerogenic property. However, the physicochemical properties and in vivo toxicity of TP still remain elusive. Rigorous clinical translation requires deciphering these vital properties. We have synthesized TP following a gold standard protocol in the traditional Siddha methodology. We assessed the size, phase, elemental constituents, and thermal stability of TP by SEM and TEM, XRD, EPR, and EDAX analyses, respectively. The results depicted the conversion of metallic copper into copper (II) oxide in the final stages of TP preparation and exhibited nanodimensions ranging between 10 and 50 nm. The XPS spectra revealed the presence of oxygen-deficient state and a carbonaceous coating was found on the surface of TP using TEM analysis. In vivo safety was studied in rat toxicity models by adopting OECD guidelines. Body weight changes, feed, and water intake were unaltered upon TP administration. Hematological, biochemical profiling, and histopathological findings also suggested its nontoxic nature with no abnormalities in major organs and its functions. Interestingly, we found that the metal toxicity could have been subdued because of the carbonaceous coating around the nanoparticle copper (II) oxide, confirming that the drug is safe at a low dose. Overall, our study has enlightened the safety of TP supporting the use of Siddha formulations.
Keywords: Siddha; Thamira parpam; copper oxide; herbometallic; nanocomplex; toxicity.
Copyright © 2022 Royapuram Parthasarathy, Manikandamathavan, Chandronitha, Vasanthi, Mohan, Vijayakumar, Shanmugam, Sekaran, Unni Nair, Chamundeeswari and Thyagarajan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures









References
-
- Alexiou C., Arnold W., Klein R. J., Parak F. G., Hulin P., Bergemann C., Locoregional Cancer Treatment with Magnetic Drug Targeting. Cancer Res. 2000; 60(23): 6641–6648. - PubMed
-
- Alyamani A. A., Albukhaty S., Aloufi S., AlMalki F. A., Al-Karagoly H., Sulaiman G. M. (2021). Green Fabrication of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Using Phlomis Leaf Extract: Characterization and In Vitro Evaluation of Cytotoxicity and Antibacterial Properties. Molecules 26 (20), 6140. 10.3390/molecules26206140 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- American Biogenics Corp (ABC) (1988). 2, 3, 4, 6-Tetrachlorophenol: 90-Day Subchronic Oral Toxicity Study in Rats Sponsored by US EPA. Office of Solid Waste Study, 410–2522.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

