Industrial Biotechnology Based on Enzymes From Extreme Environments
- PMID: 35480975
- PMCID: PMC9036996
- DOI: 10.3389/fbioe.2022.870083
Industrial Biotechnology Based on Enzymes From Extreme Environments
Abstract
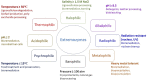
Biocatalysis is crucial for a green, sustainable, biobased economy, and this has driven major advances in biotechnology and biocatalysis over the past 2 decades. There are numerous benefits to biocatalysis, including increased selectivity and specificity, reduced operating costs and lower toxicity, all of which result in lower environmental impact of industrial processes. Most enzymes available commercially are active and stable under a narrow range of conditions, and quickly lose activity at extremes of ion concentration, temperature, pH, pressure, and solvent concentrations. Extremophilic microorganisms thrive under extreme conditions and produce robust enzymes with higher activity and stability under unconventional circumstances. The number of extremophilic enzymes, or extremozymes, currently available are insufficient to meet growing industrial demand. This is in part due to difficulty in cultivation of extremophiles in a laboratory setting. This review will present an overview of extremozymes and their biotechnological applications. Culture-independent and genomic-based methods for study of extremozymes will be presented.
Keywords: alkaliphile; extreme environment; extremozyme; halophile; metagenomics; psychrophile; single amplified genome; thermophile.
Copyright © 2022 Mesbah.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous