A novel DPH5-related diphthamide-deficiency syndrome causing embryonic lethality or profound neurodevelopmental disorder
- PMID: 35482014
- PMCID: PMC9426662
- DOI: 10.1016/j.gim.2022.03.014
A novel DPH5-related diphthamide-deficiency syndrome causing embryonic lethality or profound neurodevelopmental disorder
Erratum in
-
A novel DPH5-related diphthamide-deficiency syndrome causing embryonic lethality or profound neurodevelopmental disorder.Genet Med. 2022 Oct;24(10):2207. doi: 10.1016/j.gim.2022.07.021. Genet Med. 2022. PMID: 36205747 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Purpose: Diphthamide is a post-translationally modified histidine essential for messenger RNA translation and ribosomal protein synthesis. We present evidence for DPH5 as a novel cause of embryonic lethality and profound neurodevelopmental delays (NDDs).
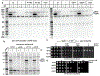
Methods: Molecular testing was performed using exome or genome sequencing. A targeted Dph5 knockin mouse (C57BL/6Ncrl-Dph5em1Mbp/Mmucd) was created for a DPH5 p.His260Arg homozygous variant identified in 1 family. Adenosine diphosphate-ribosylation assays in DPH5-knockout human and yeast cells and in silico modeling were performed for the identified DPH5 potential pathogenic variants.
Results: DPH5 variants p.His260Arg (homozygous), p.Asn110Ser and p.Arg207Ter (heterozygous), and p.Asn174LysfsTer10 (homozygous) were identified in 3 unrelated families with distinct overlapping craniofacial features, profound NDDs, multisystem abnormalities, and miscarriages. Dph5 p.His260Arg homozygous knockin was embryonically lethal with only 1 subviable mouse exhibiting impaired growth, craniofacial dysmorphology, and multisystem dysfunction recapitulating the human phenotype. Adenosine diphosphate-ribosylation assays showed absent to decreased function in DPH5-knockout human and yeast cells. In silico modeling of the variants showed altered DPH5 structure and disruption of its interaction with eEF2.
Conclusion: We provide strong clinical, biochemical, and functional evidence for DPH5 as a novel cause of embryonic lethality or profound NDDs with multisystem involvement and expand diphthamide-deficiency syndromes and ribosomopathies.
Keywords: Nonverbal neurodevelopment delays; Novel gene discovery; Precision animal modeling; Precision genomics; Translational genetics.
Copyright © 2022. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest K.G.M. is an employee of GeneDx, Inc. K.M. and U.B. are members of and employed by Roche Pharma Research & Early Development. Roche is interested in targeted therapies and diagnostics. All other authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


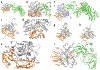
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

