Low Complexity Regions in Mammalian Proteins are Associated with Low Protein Abundance and High Transcript Abundance
- PMID: 35482425
- PMCID: PMC9070799
- DOI: 10.1093/molbev/msac087
Low Complexity Regions in Mammalian Proteins are Associated with Low Protein Abundance and High Transcript Abundance
Abstract
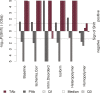
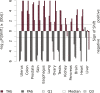
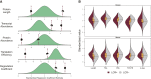
Low Complexity Regions (LCRs) are present in a surprisingly large number of eukaryotic proteins. These highly repetitive and compositionally biased sequences are often structurally disordered, bind promiscuously, and evolve rapidly. Frequently studied in terms of evolutionary dynamics, little is known about how LCRs affect the expression of the proteins which contain them. It would be expected that rapidly evolving LCRs are unlikely to be tolerated in strongly conserved, highly abundant proteins, leading to lower overall abundance in proteins which contain LCRs. To test this hypothesis and examine the associations of protein abundance and transcript abundance with the presence of LCRs, we have integrated high-throughput data from across mammals. We have found that LCRs are indeed associated with reduced protein abundance, but are also associated with elevated transcript abundance. These associations are qualitatively consistent across 12 human tissues and nine mammalian species. The differential impacts of LCRs on abundance at the protein and transcript level are not explained by differences in either protein degradation rates or the inefficiency of translation for LCR containing proteins. We suggest that rapidly evolving LCRs are a source of selective pressure on the regulatory mechanisms which maintain steady-state protein abundance levels.
Keywords: low complexity, protein abundance, transcript abundance, protein regulation.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Society for Molecular Biology and Evolution.
Figures


References
-
- Bihorel S, Baudin M. 2018. neldermead: R Port of the “Scilab” Neldermead Module. R package version 1.0-11.
-
- Brawand D, Soumillon M, Necsulea A, Julien P, Csardi G, Harrigan P, Weier M, Liechti A, Aximu-Petri A, Kircher M, et al. 2011. The evolution of gene expression levels in mammalian organs. Nature 478:343–348. - PubMed
-
- Cambridge SB, Gnad F, Nguyen C, Bermejo JL, Krüger M, Mann M. 2011. Systems-wide proteomic analysis in mammalian cells reveals conserved, functional protein turnover. J Proteome Res. 10:5275–5284. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

