Clinical advances of RNA therapeutics for treatment of neurological and neuromuscular diseases
- PMID: 35482908
- PMCID: PMC9067473
- DOI: 10.1080/15476286.2022.2066334
Clinical advances of RNA therapeutics for treatment of neurological and neuromuscular diseases
Abstract
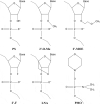
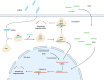
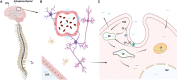
RNA therapeutics comprise a diverse group of oligonucleotide-based drugs such as antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs), small interfering RNAs (siRNAs), and short hairpin RNAs (shRNAs) that can be designed to selectively interact with drug targets currently undruggable with small molecule-based drugs or monoclonal antibodies. Furthermore, RNA-based therapeutics have the potential to modulate entire disease pathways, and thereby represent a new modality with unprecedented potential for generating disease-modifying drugs for a wide variety of human diseases, including central nervous system (CNS) disorders. Here, we describe different strategies for delivering RNA drugs to the CNS and review recent advances in clinical development of ASO drugs and siRNA-based therapeutics for the treatment of neurological diseases and neuromuscular disorders.Abbreviations 2'-MOE: 2'-O-(2-methoxyethyl); 2'-O-Me: 2'-O-methyl; 2'-F: 2'-fluoro; AD: Alzheimer's disease; ALS: Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis; ALSFRS-R: Revised Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Functional Rating Scale; ARC: Antibody siRNA Conjugate; AS: Angelman Syndrome; ASGRP: Asialoglycoprotein receptor; ASO: Antisense oligonucleotide; AxD: Alexander Disease; BBB: Blood brain barrier; Bp: Basepair; CNM: Centronuclear myopathies; CNS: Central Nervous System; CPP: Cell-penetrating Peptide; CSF: Cerebrospinal fluid; DMD: Duchenne muscular dystrophy; DNA: Deoxyribonucleic acid; FAP: Familial amyloid polyneuropathy; FALS: Familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis; FDA: The United States Food and Drug Administration; GalNAc: N-acetylgalactosamine; GoF: Gain of function; hATTR: Hereditary transthyretin amyloidosis; HD: Huntington's disease; HRQOL: health-related quality of life; ICV: Intracerebroventricular; IT: Intrathecal; LNA: Locked nucleic acid; LoF: Loss of function; mRNA: Messenger RNA; MS: Multiple Sclerosis; MSA: Multiple System Atrophy; NBE: New Biological Entity; NCE: New Chemical Entity; NHP: Nonhuman primate; nt: Nucleotide; PD: Parkinson's disease; PNP: Polyneuropathy; PNS: Peripheral nervous system; PS: Phosphorothioate; RISC: RNA-Induced Silencing Complex; RNA: Ribonucleic acid; RNAi: RNA interference; s.c.: Subcutaneous; siRNA: Small interfering RNA; SMA: Spinal muscular atrophy; SMN: Survival motor neuron; TTR: Transthyretin.
Keywords: CNS; RNA-based therapeutics; Small interfering RNA; antisense oligonucleotide; clinical trial; gene silencing; neurological disease; neuromuscular disorder.
Conflict of interest statement
S.N.H. is an employee and H.K. and S.K. are scientific cofounders of Neumirna Therapeutics, a biopharmaceutical company developing RNA-based therapeutics for neurological disorders and have shares in the company. A.H. declares no competing interests. The figures were created with BioRender.com.
Figures

References
-
- Roberts E, Frankel S.. Gamma-aminobutyric acid in brain: its formation from glutamic acid. J Biol Chem. 1950;187:55–63. - PubMed
-
- Carlsson A. Thirty years of dopamine research. Adv Neurol. 1993;60:1–10. - PubMed
-
- Vaikath NN, Hmila I, Gupta V, et al. Antibodies against alpha-synuclein: tools and therapies. J Neurochem. 2019;150:612–625. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
