Small-world connectivity dictates collective endothelial cell signaling
- PMID: 35482920
- PMCID: PMC9170162
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2118927119
Small-world connectivity dictates collective endothelial cell signaling
Abstract
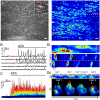
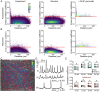
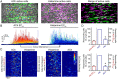
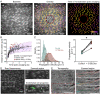
Every blood vessel is lined by a single layer of highly specialized, yet adaptable and multifunctional endothelial cells. These cells, the endothelium, control vascular contractility, hemostasis, and inflammation and regulate the exchange of oxygen, nutrients, and waste products between circulating blood and tissue. To control each function, the endothelium processes endlessly arriving requests from multiple sources using separate clusters of cells specialized to detect specific stimuli. A well-developed but poorly understood communication system operates between cells to integrate multiple lines of information and coordinate endothelial responses. Here, the nature of the communication network has been addressed using single-cell Ca2+ imaging across thousands of endothelial cells in intact blood vessels. Cell activities were cross-correlated and compared to a stochastic model to determine network connections. Highly correlated Ca2+ activities occurred in scattered cell clusters, and network communication links between them exhibited unexpectedly short path lengths. The number of connections between cells (degree distribution) followed a power-law relationship revealing a scale-free network topology. The path length and degree distribution revealed an endothelial network with a “small-world” configuration. The small-world configuration confers particularly dynamic endothelial properties including high signal-propagation speed, stability, and a high degree of synchronizability. Local activation of small clusters of cells revealed that the short path lengths and rapid signal transmission were achieved by shortcuts via connecting extensions to nonlocal cells. These findings reveal that the endothelial network design is effective for local and global efficiency in the interaction of the cells and rapid and robust communication between endothelial cells in order to efficiently control cardiovascular activity.
Keywords: calcium; endothelium; network; signaling; small-world.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures



References
-
- Zuccolo E., et al. , Glutamate triggers intracellular Ca2+ oscillations and nitric oxide release by inducing NAADP- and InsP3-dependent Ca2+ release in mouse brain endothelial cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 234, 3538–3554 (2019). - PubMed
-
- Garland C. J., et al. , Voltage-dependent Ca2+ entry into smooth muscle during contraction promotes endothelium-mediated feedback vasodilation in arterioles. Sci. Signal. 10, eaal3806 (2017). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

