Tissue remodeling by an opportunistic pathogen triggers allergic inflammation
- PMID: 35483356
- PMCID: PMC9123649
- DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2022.04.001
Tissue remodeling by an opportunistic pathogen triggers allergic inflammation
Abstract
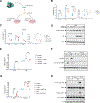
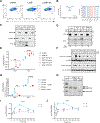
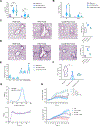
Different effector arms of the immune system are optimized to protect from different classes of pathogens. In some cases, pathogens manipulate the host immune system to promote the wrong type of effector response-a phenomenon known as immune deviation. Typically, immune deviation helps pathogens to avoid destructive immune responses. Here, we report on a type of immune deviation whereby an opportunistic pathogen, Pseudomonas aeruginosa (P. aeruginosa), induces the type 2 immune response resulting in mucin production that is used as an energy source by the pathogen. Specifically, P. aeruginosa-secreted toxin, LasB, processed and activated epithelial amphiregulin to induce type 2 inflammation and mucin production. This "niche remodeling" by P. aeruginosa promoted colonization and, as a by-product, allergic sensitization. Our study thus reveals a type of bacterial immune deviation by increasing nutrient supply. It also uncovers a mechanism of allergic sensitization by a bacterial virulence factor.
Keywords: LasB; P. aeruginosa; allergic inflammation; amphiregulin; immune deviation; lung; mucin; opportunistic pathogen; type 2 immunity.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests All authors declare no competing interests. B.V. is currently an employee of EMD Serono.
Figures




Comment in
-
Virulence triggered allergies: Pseudomonas gets the Las laugh.Immunity. 2022 May 10;55(5):824-826. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2022.04.011. Immunity. 2022. PMID: 35545032
-
Pseudomonas aeruginosa: a pathogen making itself at home.Trends Immunol. 2022 Jul;43(7):497-499. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2022.05.002. Epub 2022 May 30. Trends Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35654640
References
-
- Abebe F (2019). Synergy between Th1 and Th2 responses during Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection: A review of current understanding. Int Rev Immunol 38, 172–179. - PubMed
-
- Annunziato F, Romagnani C, and Romagnani S (2015). The 3 major types of innate and adaptive cell-mediated effector immunity. The Journal of allergy and clinical immunology 135, 626–635. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

