Postcolumn Infusion as a Quality Control Tool for LC-MS-Based Analysis
- PMID: 35483670
- PMCID: PMC10443037
- DOI: 10.1021/jasms.2c00022
Postcolumn Infusion as a Quality Control Tool for LC-MS-Based Analysis
Abstract
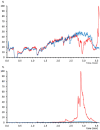
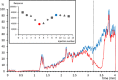
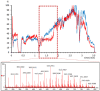
Postcolumn infusion has been widely used to study the matrix effect of analytical methods based on liquid chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry (LC-MS). Nevertheless, this methodology is usually only applied during a method development or validation. With this application note, we aim to demonstrate that the continuous use of postcolumn infusion can be also a very useful tool to monitor the quality of LC-MS analyses and easily detect flaws in the analytical method performance. Here we propose a protocol that can be transferred to other LC-MS platforms, and we show some real situations in bioanalysis in which postcolumn infusion proved to be extremely helpful in, for example, the evaluation of a sample treatment or the detection of unexpected sources of the matrix effect.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Development of an Untargeted LC-MS Metabolomics Method with Postcolumn Infusion for Matrix Effect Monitoring in Plasma and Feces.J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2024 Mar 6;35(3):590-602. doi: 10.1021/jasms.3c00418. Epub 2024 Feb 21. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2024. PMID: 38379502 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic evaluation of supported liquid extraction in reducing matrix effect and improving extraction efficiency in LC-MS/MS based bioanalysis for 10 model pharmaceutical compounds.J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2012 Apr 1;891-892:71-80. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2012.02.031. Epub 2012 Feb 23. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2012. PMID: 22410088
-
Development and validation of an LC-MS/MS method for the bioanalysis of the major metamizole metabolites in human plasma.Bioanalysis. 2020 Feb;12(3):175-189. doi: 10.4155/bio-2019-0251. Epub 2020 Feb 13. Bioanalysis. 2020. PMID: 32052638
-
Pitfalls associated with the use of liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry in the clinical laboratory.Clin Chem. 2010 Aug;56(8):1234-44. doi: 10.1373/clinchem.2009.138602. Epub 2010 May 28. Clin Chem. 2010. PMID: 20511452 Review.
-
A classification of liquid chromatography mass spectrometry techniques for evaluation of chemical composition and quality control of traditional medicines.J Chromatogr A. 2020 Jan 4;1609:460501. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2019.460501. Epub 2019 Aug 30. J Chromatogr A. 2020. PMID: 31515074 Review.
Cited by
-
Development of an Untargeted LC-MS Metabolomics Method with Postcolumn Infusion for Matrix Effect Monitoring in Plasma and Feces.J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2024 Mar 6;35(3):590-602. doi: 10.1021/jasms.3c00418. Epub 2024 Feb 21. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2024. PMID: 38379502 Free PMC article.
-
Cortisol and cortisone determination by disposable pipette extraction (DPX) and ultra-efficient liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry (UHPLC-MS/MS) in urine and saliva samples from patients with Parkinson's disease.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2024 Nov;416(28):6589-6600. doi: 10.1007/s00216-024-05557-6. Epub 2024 Sep 26. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2024. PMID: 39327306
-
Mitigating Matrix Effects in LC-ESI-MS-MS Analysis of a Urinary Biomarker of Xylenes Exposure.J Anal Toxicol. 2023 Mar 21;47(2):129-135. doi: 10.1093/jat/bkac046. J Anal Toxicol. 2023. PMID: 35766875 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kebarle P.; Tang L. From ions in solution to ions in the gas phase - the mechanism of electrospray mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 1993, 65, 972A–986A. 10.1021/ac00070a001. - DOI
-
- Hall T. G.; Smukste I.; Bresciano K. R.; Wang Y.; McKearn D.; Savage R. E.. Identifying and Overcoming Matrix Effects in Drug Discovery and Development. Tandem Mass Spectrometry - Applications and Principles ;IntechOpen Limited: London, UK, 2012; pp 389–420.10.5772/32108 - DOI
-
- Cortese M.; Gigliobianco M. R.; Magnoni F.; Censi R.; Di Martino P. Compensate for or Minimize Matrix Effects? Strategies for Overcoming Matrix Effects in Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry Technique: A Tutorial Review. Molecules 2020, 25 (13), 3047.10.3390/molecules25133047. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

