Diet or medication in primary care patients with IBS: the DOMINO study - a randomised trial supported by the Belgian Health Care Knowledge Centre (KCE Trials Programme) and the Rome Foundation Research Institute
- PMID: 35483886
- PMCID: PMC9554021
- DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2021-325821
Diet or medication in primary care patients with IBS: the DOMINO study - a randomised trial supported by the Belgian Health Care Knowledge Centre (KCE Trials Programme) and the Rome Foundation Research Institute
Abstract
Background: In Europe, IBS is commonly treated with musculotropic spasmolytics (eg, otilonium bromide, OB). In tertiary care, a low fermentable oligosaccharides, disaccharides, monosaccharides and polyols (FODMAP) diet provides significant improvement. Yet, dietary treatment remains to be explored in primary care. We evaluated the effect of a smartphone FODMAP-lowering diet application versus OB on symptoms in primary care IBS.
Methods: IBS patients, recruited by primary care physicians, were randomised to 8 weeks of OB (40 mg three times a day) or diet and followed for 24 weeks. We compared IBS Symptom Severity Score and the proportion of responders (improvement ≥50 points) in all patients and the subgroup fulfilling Rome IV criteria (Rome+). We also evaluated treatment efficacy, quality of life, anxiety, depression, somatic symptom severity (Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ15, PHQ9)) and treatment adherence and analysed predictors of response.
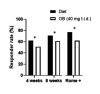
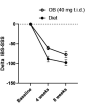
Results: 459 primary care IBS patients (41±15 years, 76% female, 70% Rome+) were randomised. The responder rate after 8 weeks was significantly higher with diet compared with OB (71% (155/218) vs 61% (133/217), p=0.03) and more pronounced in Rome+ (77% (118/153) vs 62% (98/158), p=0.004). Patients allocated to diet (199/212) were 94% adherent compared with 73% with OB (148/202) (p<0.001). The significantly higher response rate with diet was already observed after 4 weeks (62% (132/213) vs 51% (110/215), p=0.02) and a high symptom response persisted during follow-up. Predictors of response were female gender (OR=2.08, p=0.04) for diet and PHQ15 (OR=1.10, p=0.02) for OB.
Conclusion: In primary care IBS patients, a FODMAP-lowering diet application was superior to a spasmolytic agent in improving IBS symptoms. A FODMAP-lowering diet should be considered the first-line treatment for IBS in primary care.
Trial registration number: NCT04270487.
Keywords: IRRITABLE BOWEL SYNDROME; PRIMARY CARE; QUALITY OF LIFE.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2022. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: JT has given Scientific advice to Alfa Wassermann, Allergan, Christian Hansen, Danone, Grünenthal, Ironwood, Janssen, Kiowa Kirin, Menarini, Mylan, Neutec, Novartis, Noventure, Nutricia, Shionogi, Shire, Takeda, Theravance, Tramedico, Truvion, Tsumura, Zealand and Zeria Pharmaceuticals, has received research support from Shire, Sofar and Tsumura, and has served on the Speaker Bureau for Abbott, Allergan, AstraZeneca, Janssen, Kyowa Kirin, Menarini, Mylan, Novartis, Shire, Takeda, Truvion and Zeria. Funding was provided by a Methusalem grant from Leuven University to JT. HP has given scientific advice to Allergan, Danone, Menarini, Merck Serono, Shire and Zeria and has served on the speaker Bureau of Menarini, Merck Serono, Shire and Zeria. LVO has given scientific advice to Danone and received research support from Nestlé. TV has given scientific advice to VectivBio, Shire, Dr. Falk Pharma, Takeda and Baxter; has received research support from Danone, MyHealth and VectivBio; and has served on the Speaker Bureau for Abbott, Tramedico, Truvion, Will Pharma, My Health, Kyowa Kirin, Menarini, Biocodex, Remedus, Fresenius Kabi and Dr. Falk Pharma. CM has served on the Speaker Bureau for Coca-Cola and Zespri and received travel/conference grants from Danone, Nestlé Health Sciences, Fresenius Kabi. This study was supported by a research grant from the Belgian Health Care Knowledge Centre (KCE). Questionnaires in this trial were developed, translated and provided by the Rome Foundation Research Institute.
Figures
Comment in
-
Further research needed to determine first-line therapy for IBS in primary care.Gut. 2023 May;72(5):1024-1025. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2022-328047. Epub 2022 Jun 22. Gut. 2023. PMID: 35732423 No abstract available.
-
In IBS, a smartphone application for self-managing a FODMAP-lowering diet vs. otilonium bromide reduced symptoms at 8 wk.Ann Intern Med. 2022 Aug;175(8):JC91. doi: 10.7326/J22-0059. Epub 2022 Aug 2. Ann Intern Med. 2022. PMID: 35914257
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
