Hypoxia-activated neuropeptide Y/Y5 receptor/RhoA pathway triggers chromosomal instability and bone metastasis in Ewing sarcoma
- PMID: 35484119
- PMCID: PMC9051212
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-29898-x
Hypoxia-activated neuropeptide Y/Y5 receptor/RhoA pathway triggers chromosomal instability and bone metastasis in Ewing sarcoma
Erratum in
-
Publisher Correction: Hypoxia-activated neuropeptide Y/Y5 receptor/RhoA pathway triggers chromosomal instability and bone metastasis in Ewing sarcoma.Nat Commun. 2022 May 12;13(1):2729. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-30473-7. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 35550518 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
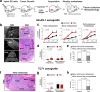
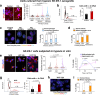
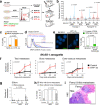
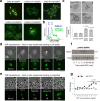
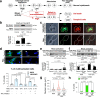
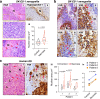
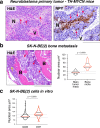
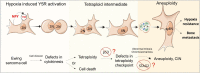
Adverse prognosis in Ewing sarcoma (ES) is associated with the presence of metastases, particularly in bone, tumor hypoxia and chromosomal instability (CIN). Yet, a mechanistic link between these factors remains unknown. We demonstrate that in ES, tumor hypoxia selectively exacerbates bone metastasis. This process is triggered by hypoxia-induced stimulation of the neuropeptide Y (NPY)/Y5 receptor (Y5R) pathway, which leads to RhoA over-activation and cytokinesis failure. These mitotic defects result in the formation of polyploid ES cells, the progeny of which exhibit high CIN, an ability to invade and colonize bone, and a resistance to chemotherapy. Blocking Y5R in hypoxic ES tumors prevents polyploidization and bone metastasis. Our findings provide evidence for the role of the hypoxia-inducible NPY/Y5R/RhoA axis in promoting genomic changes and subsequent osseous dissemination in ES, and suggest that targeting this pathway may prevent CIN and disease progression in ES and other cancers rich in NPY and Y5R.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

