Global population attributable fraction of potentially modifiable risk factors for mental disorders: a meta-umbrella systematic review
- PMID: 35484237
- PMCID: PMC9708560
- DOI: 10.1038/s41380-022-01586-8
Global population attributable fraction of potentially modifiable risk factors for mental disorders: a meta-umbrella systematic review
Abstract
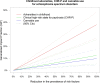
Numerous risk factors for mental disorders have been identified. However, we do not know how many disorders we could prevent and to what extent by modifying these risk factors. This study quantifies the Population Attributable Fraction (PAF) of potentially modifiable risk factors for mental disorders. We conducted a PRISMA 2020-compliant (Protocol: https://osf.io/hk2ag ) meta-umbrella systematic review (Web of Science/PubMed/Cochrane Central Register of Reviews/Ovid/PsycINFO, until 05/12/2021) of umbrella reviews reporting associations between potentially modifiable risk factors and ICD/DSM mental disorders, restricted to highly convincing (class I) and convincing (class II) evidence from prospective cohorts. The primary outcome was the global meta-analytical PAF, complemented by sensitivity analyses across different settings, the meta-analytical Generalised Impact Fraction (GIF), and study quality assessment (AMSTAR). Seven umbrella reviews (including 295 meta-analyses and 547 associations) identified 28 class I-II risk associations (23 risk factors; AMSTAR: 45.0% high-, 35.0% medium-, 20.0% low quality). The largest global PAFs not confounded by indication were 37.84% (95% CI = 26.77-48.40%) for childhood adversities and schizophrenia spectrum disorders, 24.76% (95% CI = 13.98-36.49%) for tobacco smoking and opioid use disorders, 17.88% (95% CI = not available) for job strain and depression, 14.60% (95% CI = 9.46-20.52%) for insufficient physical activity and Alzheimer's disease, 13.40% (95% CI = 7.75-20.15%) for childhood sexual abuse and depressive disorders, 12.37% (95% CI = 5.37-25.34%) for clinical high-risk state for psychosis and any non-organic psychotic disorders, 10.00% (95% CI = 5.62-15.95%) for three metabolic factors and depression, 9.73% (95% CI = 4.50-17.30%) for cannabis use and schizophrenia spectrum disorders, and 9.30% (95% CI = 7.36-11.38%) for maternal pre-pregnancy obesity and ADHD. The GIFs confirmed the preventive capacity for these factors. Addressing several potentially modifiable risk factors, particularly childhood adversities, can reduce the global population-level incidence of mental disorders.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. Arango has been a consultant to or has received honoraria or grants from Acadia, Angelini, Boehringer, Gedeon Richter, Janssen Cilag, Lundbeck, Minerva, Otsuka, Pfizer, Roche, Sage, Servier, Shire, Schering Plough, Sumitomo Dainippon Pharma, Sunovion and Takeda outside the current work. Paolo Fusar-Poli has received research or personal fees from Lundbeck, Angelini, Menarini and Boehringer Ingelheim outside the current work. Dr. Correll has been a consultant and/or advisor to or has received honoraria from AbbVie, Acadia, Alkermes, Allergan, Angelini, Aristo, Axsome, Damitsa, Gedeon Richter, Hikma, IntraCellular Therapies, Janssen/J&J, Karuna, LB Pharma, Lundbeck, MedAvante-ProPhase, MedInCell, Medscape, Merck, Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma, Mylan, Neurocrine, Noven, Otsuka, Pfizer, Recordati, Rovi, Servier, SK Life Science, Sumitomo Dainippon, Sunovion, Supernus, Takeda, Teva, and Viatris. He provided expert testimony for Janssen and Otsuka. He served on a Data Safety Monitoring Board for Lundbeck, Rovi, Supernus, and Teva. He has received grant support from Janssen and Takeda. He received royalties from UpToDate and is also a stock option holder of LB Pharma. Dr. Jones is funded by the NIHR ARC East of England. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures