Copy number alterations define outcome in Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia
- PMID: 35484650
- PMCID: PMC9335102
- DOI: 10.3324/haematol.2021.280578
Copy number alterations define outcome in Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia
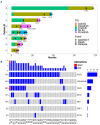
Figures

References
-
- Soverini S, Benedittis CD, Polakova KM, et al. Unraveling the complexity of tyrosine kinase inhibitor–resistant populations by ultra-deep sequencing of the BCR-ABL kinase domain. Blood. 2013;122(9):1634-1648. - PubMed
-
- Foà R, Bassan R, Vitale A, et al. Dasatinib–blinatumomab for Ph-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia in adults. N Engl J Med. 2020;383(17):1613-1623. - PubMed
-
- Chang J, Douer D, Aldoss I, et al. Combination chemotherapy plus dasatinib leads to comparable overall survival and relapse free survival rates as allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in Philadelphia positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Cancer Med. 2019;8(6):2832-2839. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

