A digital intervention using virtual reality helmets to reduce dental anxiety of children under local anesthesia and primary teeth extraction: A randomized clinical trial
- PMID: 35485000
- PMCID: PMC9226823
- DOI: 10.1002/brb3.2600
A digital intervention using virtual reality helmets to reduce dental anxiety of children under local anesthesia and primary teeth extraction: A randomized clinical trial
Abstract
Introduction: Behavior management of children during dental treatment is an important but challenging issue. As a new technique, VR has been applied in pediatric dental anxiety. But there is no final conclusion whether VR reduces children's dental anxiety.
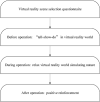
Methods: The aim of the study is to assess the effectiveness of a digital intervention using virtual reality (VR) helmets on dental anxiety, pain perception, and behavior triggered for children, as well as occurrence of simulator sickness in local anesthesia and primary teeth extraction. A total of 128 children, who needed primary teeth extraction under local anesthesia, were randomly allocated into two groups: use VR helmets and traditional behavior guidance procedures (control). Modified Child Fear Survey Schedule Dental Subscale (CFSS-DS), Wong-Baker FACES Pain Scale, Houpt Scale, and Simulator sickness questionnaire (SSQ) were used to assess children's dental anxiety, pain perception, and behavior triggered and occurrence of simulator sickness.
Results: CFSS-DS score in the VR group was significantly decreased after dental treatment (34.58±6.90 before operation and 32.32±15.58 after operation, p = .02). The score of Wong Baker Scale in the VR group (3.47±0.76) was significantly lower than that in the control group (5.56±1.13, p = .015). There was no significant difference in the Houpt Behavior Scale score and the SSQ score between the VR group and the control group (p = .35, p = .305).
Conclusion: The use of VR helmets in primary teeth extraction can significantly reduce dental anxiety and pain perception in children without occurrence of simulator sickness.
Keywords: child behavior; dental anxiety; distraction systems; pain perception; virtual reality exposure therapy.
© 2022 The Authors. Brain and Behavior published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Application of virtual reality on non-drug behavioral management of short-term dental procedure in children.Trials. 2021 Aug 23;22(1):562. doi: 10.1186/s13063-021-05540-x. Trials. 2021. PMID: 34425901 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Clinical evaluation of feasibility and effectiveness using a virtual reality device during local anesthesia and extractions in pediatric patients.Eur Arch Paediatr Dent. 2023 Jun;24(3):379-386. doi: 10.1007/s40368-023-00801-6. Epub 2023 May 15. Eur Arch Paediatr Dent. 2023. PMID: 37184588 Clinical Trial.
-
Use of Virtual Reality in the Pediatric Perioperative Setting and for Induction of Anesthesia: Mixed Methods Pilot Feasibility Study.JMIR Perioper Med. 2025 May 16;8:e58905. doi: 10.2196/58905. JMIR Perioper Med. 2025. PMID: 40378405 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness of Virtual Reality Glasses as a Distraction for Children During Dental Care.Pediatr Dent. 2020 Mar 15;42(2):93-102. Pediatr Dent. 2020. PMID: 32276674 Review.
-
The effect of virtual reality for anxiety and pain in dentistry: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Community Dent Health. 2024 Nov 29;41(4):248-255. doi: 10.1922/CDH_00160Nezhad08. Community Dent Health. 2024. PMID: 39535423
Cited by
-
The Role of Family Factors in the Development of Dental Anxiety in Children.Medicina (Kaunas). 2024 Jan 19;60(1):180. doi: 10.3390/medicina60010180. Medicina (Kaunas). 2024. PMID: 38276059 Free PMC article.
-
Analyzing Nonpharmacological Behavior Management in Children With Dental Anxiety: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Health Sci Rep. 2025 Aug 19;8(8):e71176. doi: 10.1002/hsr2.71176. eCollection 2025 Aug. Health Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40843385 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Virtual reality and behaviour management in paediatric dentistry: a systematic review.BMC Oral Health. 2023 Dec 12;23(1):995. doi: 10.1186/s12903-023-03595-7. BMC Oral Health. 2023. PMID: 38087294 Free PMC article.
-
Moving toward Fear-Free Husbandry and Veterinary Care for Horses.Animals (Basel). 2022 Oct 24;12(21):2907. doi: 10.3390/ani12212907. Animals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36359031 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of Virtual Reality Intervention on Anxiety and Level of Cooperation in Children and Adolescents with Autism Spectrum Disorder during the Dental Examination.J Clin Med. 2024 Oct 12;13(20):6093. doi: 10.3390/jcm13206093. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 39458041 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Attar, R. H. , & Baghdadi, Z. D. (2015). Comparative efficacy of active and passive distraction during restorative treatment in children using an iPad versus audiovisual eyeglasses: A randomised controlled trial. European Archives of Paediatric Dentistry, 16, 1–8. 10.1007/s40368-014-0136-x - DOI - PubMed
-
- American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry . (2011). Behavior Guidance for the Pediatric Dental Patient. Pediatric Dentistry, 36, 179–191.
-
- American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry . (2018). Behavior Guidance for the Pediatric Dental Patient. Pediatric Dentistry, 40, 254–267. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

