Time Course and Risk Profile of Work-Related Neck Disability: A Longitudinal Latent Class Growth Analysis
- PMID: 35485191
- PMCID: PMC9350532
- DOI: 10.1093/ptj/pzac050
Time Course and Risk Profile of Work-Related Neck Disability: A Longitudinal Latent Class Growth Analysis
Abstract
Objective: Given the economic burden of work-related neck pain and disability, it is important to understand its time course and associated risk factors to direct better management strategies. This study aimed to identify the 1-year trajectories of work-related neck disability in a high-risk occupation group such as sonography and to investigate which baseline biopsychosocial factors are associated with the identified trajectories.
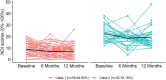
Methods: A longitudinal study was conducted among 92 sonographers with neck disability assessed at 3 time points-baseline, 6 months, and 12 months-using the Neck Disability Index. Baseline biopsychosocial measures included individual characteristics (demographics and physical activity levels), work-related physical and psychosocial factors (eg, ergonomic risk, workplace social support, job satisfaction), general psychological features (depression, anxiety, pain catastrophizing, and fear-avoidance beliefs), and quantitative sensory testing of somatosensory function (cold and pressure pain thresholds at neck and tibialis anterior, and temporal summation).
Results: Two distinct trajectories of neck disability were identified, including a "low-resolving disability" trajectory showing slow improvement toward no disability (64.8%) and a "moderate-fluctuating disability" trajectory characterized by persistent moderate disability with a small fluctuation across time (35.2%). The trajectory of moderate-fluctuating disability was associated with more severe symptoms, lower vigorous physical activity, higher ergonomic risk, remote cold hyperalgesia, widespread mechanical hyperalgesia, heightened pain facilitation, and several psychosocial factors such as anxiety, depression, lower job satisfaction, and lower workplace social support at baseline.
Conclusion: Over one-third of sonographers were at risk of developing a moderate-fluctuating disability trajectory. This unfavorable trajectory was associated with low physical activity level, poor ergonomics, psychosocial distress, and central sensitization at baseline.
Impact: This study has important implications for the management of neck disability in workers. Addressing modifiable factors including low vigorous physical activity, poor ergonomics, anxiety, depression, and lack of workplace social support may improve the trajectory of work-related neck disability.
Keywords: Biopsychosocial Risk; Central Sensitization; Disability Trajectory; Neck Pain; Prospective Study; Quantitative Sensory Testing.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the American Physical Therapy Association. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Heightened pain facilitation rather than impaired pain inhibition distinguishes those with moderate/severe disability in work-related neck pain.Pain. 2021 Aug 1;162(8):2225-2236. doi: 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000002213. Pain. 2021. PMID: 33534358
-
Disability Trajectories in Patients With Complaints of Arm, Neck, and Shoulder (CANS) in Primary Care: Prospective Cohort Study.Phys Ther. 2016 Jul;96(7):972-84. doi: 10.2522/ptj.20150226. Epub 2015 Dec 4. Phys Ther. 2016. PMID: 26637644
-
Repositioning error, pressure pain threshold, catastrophizing and anxiety in adolescents with chronic idiopathic neck pain.Musculoskelet Sci Pract. 2017 Aug;30:18-24. doi: 10.1016/j.msksp.2017.04.011. Epub 2017 May 1. Musculoskelet Sci Pract. 2017. PMID: 28494262
-
Comparing Central Pain Processing in Individuals With Non-Traumatic Neck Pain and Healthy Individuals: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Pain. 2020 Nov-Dec;21(11-12):1101-1124. doi: 10.1016/j.jpain.2020.02.007. Epub 2020 Jun 20. J Pain. 2020. PMID: 32574788
-
Relationships Between Psychological, Sleep, and Physical Activity Measures and Somatosensory Function in People With Peripheral Joint Pain: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Pain Pract. 2021 Feb;21(2):226-261. doi: 10.1111/papr.12943. Epub 2020 Sep 5. Pain Pract. 2021. PMID: 32696604
Cited by
-
A new approach for the implementation of ergonomics in sonography to prevent work-related musculoskeletal disorders (ErgoSon).J Occup Med Toxicol. 2025 Apr 7;20(1):11. doi: 10.1186/s12995-025-00457-6. J Occup Med Toxicol. 2025. PMID: 40197303 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic Inflammation, Sleep, and Psychological Factors Determine Recovery Trajectories for People With Neck Pain: An Exploratory Study.J Pain. 2024 Aug;25(8):104496. doi: 10.1016/j.jpain.2024.02.010. Epub 2024 Feb 9. J Pain. 2024. PMID: 38342190 Free PMC article.
-
Occupational biopsychosocial factors associated with neck pain intensity, neck-disability, and sick leave: A cross-sectional study of construction labourers in an African population.PLoS One. 2024 Apr 3;19(4):e0295352. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0295352. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38568955 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of neck posture and insulating stick use on neck disability in Korean line workers: a cross-sectional study.Ann Occup Environ Med. 2024 Apr 15;36:e11. doi: 10.35371/aoem.2024.36.e11. eCollection 2024. Ann Occup Environ Med. 2024. PMID: 38741681 Free PMC article.
-
Increase in Strength After Multimodal Pain Management Concept in Patients with Cervical Radiculopathy-A Non-Randomized, Uncontrolled Clinical Trial.Medicina (Kaunas). 2024 Nov 28;60(12):1961. doi: 10.3390/medicina60121961. Medicina (Kaunas). 2024. PMID: 39768842 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Barros-Gomes S, Orme N, Nhola LF, et al. Characteristics and consequences of work-related musculoskeletal pain among cardiac sonographers compared with peer employees: a multisite cross-sectional study. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2019;32:1138–1146. - PubMed
-
- Gremark Simonsen J, Axmon A, Nordander C, Arvidsson I. Neck and upper extremity pain in sonographers - associations with occupational factors. Appl Ergon. 2017;58:245–253. - PubMed
-
- Xie Y, Coombes BK, Thomas L, Johnston V. Musculoskeletal pain and disability in sonographers: more than an ergonomic issue. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2020;33:1526–1527. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

