Pertussis surveillance results from a French general practitioner network, France, 2017 to 2020
- PMID: 35485270
- PMCID: PMC9052767
- DOI: 10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2022.27.17.2100515
Pertussis surveillance results from a French general practitioner network, France, 2017 to 2020
Abstract
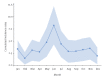
IntroductionIn France, three complementary surveillance networks involving hospitals and paediatrician practices currently allow pertussis surveillance among infants (<1 year old) and children (1-12 years old). Data on incidences among adolescents (13-17 years old) and adults (≥ 18 years) are scarce. In 2017, a sentinel surveillance system called Sentinelles network, was implemented among general practitioners (GPs).AimThe purpose of Sentinelles network is to assess pertussis incidence, monitor the cases' age distribution and evaluate the impact of the country's vaccination policy. We present the results from the first 4 years of this surveillance.MethodsGPs of the French Sentinelles network reported weekly numbers of epidemiologically or laboratory-confirmed cases and their characteristics.ResultsA total of 132 cases were reported over 2017-2020. Estimated national incidence rates per 100,000 inhabitants were 17 (95% confidence interval (CI): 12-22) in 2017, 10 (95% CI: 6-14) in 2018, 15 (95% CI: 10-20) in 2019 and three (95% CI: 1-5) in 2020. The incidence rate was significantly lower in 2020 than in 2017-2019. Women were significantly more affected than men (83/132; 63% of women, p = 0.004); 66% (87/132) of cases were aged 15 years or over (median age: 31.5 years; range: 2 months-87 years). Among 37 vaccinated cases with data, 33 had received the recommended number of doses for their age.ConclusionsThese results concur with incidences reported in other European countries, and with studies showing that the incidences of several respiratory diseases decreased in 2020 during the COVID-19 pandemic. The results also suggest a shift of morbidity towards older age groups, and a rapid waning of immunity after vaccination, justifying to continue this surveillance.
Keywords: Bordetella; France; pertussis vaccine; sentinel network; surveillance; whooping cough.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Guiso N, de La Rocque F, Njamkepo E, Lécuyer A, Levy C, Romain O, et al. French Pediatrics Groups Association Clinique et Thérapeutique Infantile du Val de Marne and Association Française de Pédiatrie Ambulatoire . Pertussis surveillance in private pediatric practices, France, 2002-2006. Emerg Infect Dis. 2008;14(7):1159-61. 10.3201/eid1407.071246 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Karsenty J-Y, Roure C, Vidal-Trecan G. La coqueluche en France. [Whooping cough in France]. BEH. 1990;19.
-
- Bégué P, Grimpel E, Roure C, Guiso N. La coqueluche en France: Nécessité de mise en place d'une surveillance. [Whooping cough in France: need for establishing a surveillance system]. BEH. 1992;48.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical