Stem Cell Therapy for Neuroprotection in the Growth-Restricted Newborn
- PMID: 35485440
- PMCID: PMC9052430
- DOI: 10.1093/stcltm/szac005
Stem Cell Therapy for Neuroprotection in the Growth-Restricted Newborn
Abstract
Fetal growth restriction (FGR) occurs when a fetus is unable to grow normally due to inadequate nutrient and oxygen supply from the placenta. Children born with FGR are at high risk of lifelong adverse neurodevelopmental outcomes, such as cerebral palsy, behavioral issues, and learning and attention difficulties. Unfortunately, there is no treatment to protect the FGR newborn from these adverse neurological outcomes. Chronic inflammation and vascular disruption are prevalent in the brains of FGR neonates and therefore targeted treatments may be key to neuroprotection. Tissue repair and regeneration via stem cell therapies have emerged as a potential clinical intervention for FGR babies at risk for neurological impairment and long-term disability. This review discusses the advancement of research into stem cell therapy for treating neurological diseases and how this may be extended for use in the FGR newborn. Leading preclinical studies using stem cell therapies in FGR animal models will be highlighted and the near-term steps that need to be taken for the development of future clinical trials.
Keywords: endothelial progenitor cells; fetal growth retardation; mesenchymal stromal cells; newborn brain; stem cells.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures
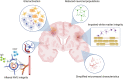
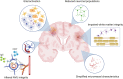
References
-
- Gordijn SJ, Beune IM, Thilaganathan B, et al. Consensus definition of fetal growth restriction: a Delphi procedure. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2016;48(3):333-339. - PubMed
-
- Sankaran S, Kyle PM. Aetiology and pathogenesis of IUGR. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 2009;23(6):765-777. - PubMed
-
- Gordijn SJ, Beune IM, Ganzevoort W. Building consensus and standards in fetal growth restriction studies. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 2018;49:117-126. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

