Imaging of the pial arterial vasculature of the human brain in vivo using high-resolution 7T time-of-flight angiography
- PMID: 35486089
- PMCID: PMC9150892
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.71186
Imaging of the pial arterial vasculature of the human brain in vivo using high-resolution 7T time-of-flight angiography
Abstract
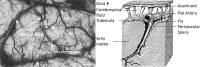
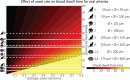
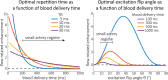
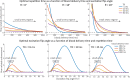
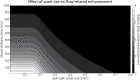
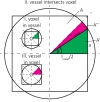
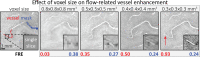
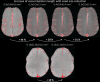
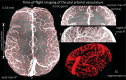
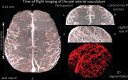
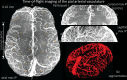
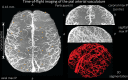
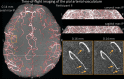
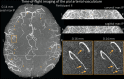
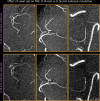
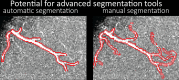
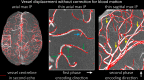
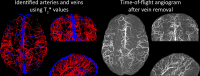
The pial arterial vasculature of the human brain is the only blood supply to the neocortex, but quantitative data on the morphology and topology of these mesoscopic arteries (diameter 50-300 µm) remains scarce. Because it is commonly assumed that blood flow velocities in these vessels are prohibitively slow, non-invasive time-of-flight magnetic resonance angiography (TOF-MRA)-which is well suited to high 3D imaging resolutions-has not been applied to imaging the pial arteries. Here, we provide a theoretical framework that outlines how TOF-MRA can visualize small pial arteries in vivo, by employing extremely small voxels at the size of individual vessels. We then provide evidence for this theory by imaging the pial arteries at 140 µm isotropic resolution using a 7 Tesla (T) magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scanner and prospective motion correction, and show that pial arteries one voxel width in diameter can be detected. We conclude that imaging pial arteries is not limited by slow blood flow, but instead by achievable image resolution. This study represents the first targeted, comprehensive account of imaging pial arteries in vivo in the human brain. This ultra-high-resolution angiography will enable the characterization of pial vascular anatomy across the brain to investigate patterns of blood supply and relationships between vascular and functional architecture.
Keywords: blood flow; blood vessel; cerebrovasculature; human; magnetic resonance angiography; magnetic resonance imaging; neuroscience; ultra-high field.
© 2022, Bollmann et al.
Conflict of interest statement
SB, HM, MB, SR, DP, OS, JP No competing interests declared
Figures

References
-
- Alsop DC, Detre JA, Golay X, Günther M, Hendrikse J, Hernandez-Garcia L, Lu H, MacIntosh BJ, Parkes LM, Smits M, van Osch MJP, Wang DJJ, Wong EC, Zaharchuk G. Recommended implementation of arterial spin-labeled perfusion MRI for clinical applications: A consensus of the ISMRM perfusion study group and the European consortium for ASL in dementia. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine. 2015;73:102–116. doi: 10.1002/mrm.25197. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01 MH124004/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EB019437/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EB032746/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- U19 NS123717/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 NS106706/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH111419/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U54 MH118919/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH111438/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG074008/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P41 EB015896/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- P41 EB030006/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- S10 RR019371/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

