Plasma arylsulfatase A levels are associated with cognitive function in Parkinson's disease
- PMID: 35486332
- PMCID: PMC9349122
- DOI: 10.1007/s10072-022-06093-w
Plasma arylsulfatase A levels are associated with cognitive function in Parkinson's disease
Abstract
Background: Arylsulfatase A (ARSA), a lysosomal enzyme, has been shown to inhibit the aggregation and propagation of α-synuclein (α-syn) through its molecular chaperone function. The relationship between ARSA levels and Parkinson's disease (PD) in the Chinese Han population remains controversial, and few quantitative research studies have investigated the relationship between plasma ARSA levels and PD.
Objectives: The purpose of this study was to investigate the relationships between ARSA levels and cognitive function in PD patients and to evaluate the association of ARSA and α-syn levels with nonmotor symptoms.
Methods: Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) was used to measure the plasma ARSA and α-syn levels in 50 healthy controls, 120 PD patients (61 PD patients with no cognitive impairment (PD-NCI) and 59 PD patients with cognitive impairment (PD-CI)). Motor symptoms and nonmotor symptoms (cognitive function, Unified Parkinson's Disease Rating Scale (UPDRS) score, depression, anxiety, constipation, olfactory dysfunction, sleep disruption, and other symptoms) were assessed with the relevant scales. The Kruskal-Wallis H test was used for comparison between groups, and Pearson/Spearman analysis was used for correlation analysis.
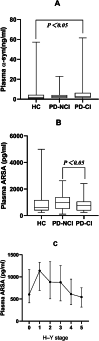
Results: The plasma ARSA concentrations were lower in the PD-CI group than in the PD-NCI group. The plasma α-syn levels in the PD-CI group were higher than those in the healthy control group, and the plasma ARSA levels were correlated with the Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE scores) and Hoehn and Yahr (H-Y) stage.
Conclusion: We used a quantitative assessment method to show that low plasma ARSA levels and high α-syn levels are related to cognitive impairment in PD patients. Plasma ARSA levels gradually decrease with PD progression.
Keywords: Arylsulfatase A; Cognitive function; Parkinson’s disease; α-Synuclein.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Pan HX, Wang YG, Zhao YW, Zeng Q, Wang Z, Fang ZH, Zhang Y, Zhou X et al (2022) Evaluating the role of ARSA in Chinese patients with Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 109:269–272. 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2021.08.008 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

