Toll-like Receptor 9 Pathway Mediates Schlafen+-MDSC Polarization During Helicobacter-induced Gastric Metaplasias
- PMID: 35487288
- PMCID: PMC9329252
- DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2022.04.031
Toll-like Receptor 9 Pathway Mediates Schlafen+-MDSC Polarization During Helicobacter-induced Gastric Metaplasias
Abstract
Background & aims: A subset of myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) that express murine Schlafen4 (SLFN4) or its human ortholog SLFN12L polarize in the Helicobacter-inflamed stomach coincident with intestinal or spasmolytic polypeptide-expressing metaplasia. We propose that individuals with a more robust response to damage-activated molecular patterns and increased Toll-like receptor 9 (TLR9) expression are predisposed to the neoplastic complications of Helicobacter infection.
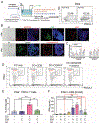
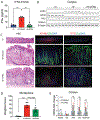
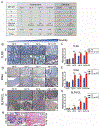
Methods: A mouse or human Transwell co-culture system composed of dendritic cells (DCs), 2-dimensional gastric epithelial monolayers, and Helicobacter were used to dissect the cellular source of interferon-α (IFNα) in the stomach by flow cytometry. Conditioned media from the co-cultures polarized primary myeloid cells. MDSC activity was determined by T-cell suppression assays. In human subjects with intestinal metaplasia or gastric cancer, the rs5743836 TLR9T>C variant was genotyped and linked to TLR9, IFNα, and SLFN12L expression by immunohistochemistry. Nuclear factor-κB binding to the TLR9 C allele was determined by electrophoretic mobility shift assays.
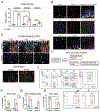
Results: Helicobacter infection induced gastric epithelial and plasmacytoid DC expression of TLR9 and IFNα. Co-culturing primary mouse or human cells with DCs and Helicobacter induced TLR9, IFNα secretion, and SLFN+-MDSC polarization. Neutralizing IFNα in vivo mitigated Helicobacter-induced spasmolytic polypeptide-expressing metaplasia. The TLR9 minor C allele creates a nuclear factor-κB binding site associated with higher levels of TLR9, IFNα, and SLFN12L in Helicobacter-infected stomachs that correlated with a greater incidence of metaplasias and cancer.
Conclusions: TLR9 plays an essential role in the production of IFNα and polarization of SLFN+ MDSCs on Helicobacter infection. Subjects carrying the rs5743836 TLR9 minor C allele are predisposed to neoplastic complications if chronically infected.
Keywords: 2-D Organoid-Derived Monolayer; DAMPs; IFNα; Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cells; SPEM.
Copyright © 2022 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Schwarz DA, Katayama CD, Hedrick SM. Schlafen, a new family of growth regulatory genes that affect thymocyte development. Immunity 1998;9:657–68. - PubMed
-
- Geserick P, Kaiser F, Klemm U, et al. Modulation of T cell development and activation by novel members of the Schlafen (slfn) gene family harbouring an RNA helicase-like motif. Int Immunol 2004;16:1535–48. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

