Chronic inflammation and calciphylaxis
- PMID: 35487645
- PMCID: PMC9058681
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2021-248668
Chronic inflammation and calciphylaxis
Abstract
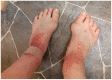
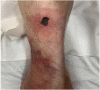
Calciphylaxis also known as calcific uraemic arteriolopathy is a rare condition mostly seen in patients with end-stage kidney disease. We report a case of a simultaneous-kidney-pancreas transplant patient with functioning grafts developing biopsy-proven calciphylaxis in the setting of chronic inflammation. Despite several modalities of management, the patient developed progression of her disease leading to multiple amputations. This case illustrates chronic inflammation driven by persistent infection as a probable contributing factor to the development and progression of calciphylaxis in a simultaneous kidney-pancreas recipient. Calciphylaxis should be considered in the differential for a painful, non-healing ulcer even in the absence of common risk factors.
Keywords: Immunology; Renal transplantation.
© BMJ Publishing Group Limited 2022. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources