Targeting IL8 as a sequential therapy strategy to overcome chemotherapy resistance in advanced gastric cancer
- PMID: 35487914
- PMCID: PMC9055054
- DOI: 10.1038/s41420-022-01033-1
Targeting IL8 as a sequential therapy strategy to overcome chemotherapy resistance in advanced gastric cancer
Abstract
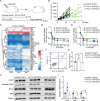
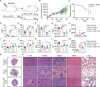
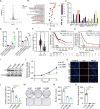
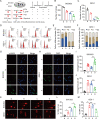
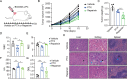
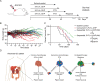
Systemic chemotherapy with multiple drug regimens is the main therapy option for advanced gastric cancer (GC) patients. However, many patients develop relapse soon. Here, we evaluated the therapeutic potential of targeting interleukin-8 (IL8) to overcome resistance to chemotherapy in advanced GC. RNA sequencing revealed crucial molecular changes after chemotherapy resistance, in which the expression of IL8 was significantly activated with the increase in drug resistance. Subsequently, the clinical significance of IL8 expression was determined in GC population specimens. IL8-targeted by RNA interference or reparixin reversed chemotherapy resistance with limited toxicity in vivo and vitro experiments. Sequential treatment with first-line, second-line chemotherapy and reparixin inhibited GC growth, reduced toxicity and prolonged survival. Collectively, our study provides a therapeutic strategy that targeting IL8 as a sequential therapy after chemotherapy resistance in advanced GC.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Kang YK, Chin K, Chung HC, Kadowaki S, Oh SC, Nakayama N, et al. S-1 plus leucovorin and oxaliplatin versus S-1 plus cisplatin as first-line therapy in patients with advanced gastric cancer (SOLAR): a randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2020;21:1045–56. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(20)30315-6. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Muro K, Van Cutsem E, Narita Y, Pentheroudakis G, Baba E, Li J, et al. Pan-Asian adapted ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for the management of patients with metastatic gastric cancer: a JSMO-ESMO initiative endorsed by CSCO, KSMO, MOS, SSO and TOS. Ann Oncol. 2019;30:19–33. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdy502. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

