Effects of conservation tillage strategies on soil physicochemical indicators and N2O emission under spring wheat monocropping system conditions
- PMID: 35487963
- PMCID: PMC9054807
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-11391-6
Effects of conservation tillage strategies on soil physicochemical indicators and N2O emission under spring wheat monocropping system conditions
Abstract
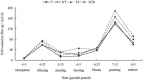
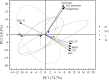
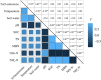
As one of the important greenhouse gas, nitrous oxide (N2O) has attracted much attention globally under climate change context. Agricultural practices are the main sources of greenhouse gas emissions. Nevertheless, scarcity of literature is available on the effects of different tillage measures on soil N2O emission under spring wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) ecosystem in the semi-arid area of the Loess Plateau. The main objective of the experimental study was to explore the influence of conservation tillage techniques on soil physicochemical properties, nitrous oxide emission and yield in the Northern semi-arid Dingxi region of China. Four treatments viz., conventional tillage (CT), no tillage (NT), straw mulch with conventional tillage (TS) and stubble-return with no-till (NTS) were evaluated under randomized complete block design with three replications. Our results depicted that compared with conventional tillage, bulk density and water content of topsoil was increased and soil pH value was reduced under conservation tillage techniques. Conservation tillage NT, TS and NTS increased organic carbon, TN, MBN and NH4+-N and reduced the accumulation of NO3-N. Additionally, although the N2O emission under NT, TS and NTS was 8.95, 41.90 and 21.05% respectively higher than under T treatment, the corresponding wheat yield was 15.40, 31.97 and 63.21% higher than T treatment. Moreover, correlation analysis showed that soil moisture and temperature were the most significant factors affecting soil N2O emission. The NTS treatment pointedly increased crop yield without significantly increasing soil N2O emission. Consequently, based on economic and environmental benefits and considering N2O emission and crop yield, we suggest that NTS technique is the best conservation tillage strategy in the semi-arid environmental zone of the Loess Plateau of Dingxi China.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Fu CH, et al. Relationships among fisheries exploitation, environmental conditions, and ecological indicators across a series of marine ecosystems. J. Mar. Syst. 2015;148:101–111. doi: 10.1016/j.jmarsys.2015.01.004. - DOI
-
- Too CC, Ong KS, Yule CM, Keller A. Putative roles of bacteria in the carbon and nitrogen cycles in a tropical peat swamp fores. Basic Appl. Ecol. 2020;52:109–123. doi: 10.1016/j.baae.2020.10.004. - DOI
-
- Hou RJ, et al. Effects of biochar and straw on greenhouse gas emission and its response mechanism in seasonally frozen farmland ecosystems. Catena. 2020;194:104735. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2020.104735. - DOI
-
- Tang ZM, Liu XR, Zhang QW, Li GC. Effects of biochar and straw on soil N2O emission from a wheat maize rotation system. Huan Jing Ke Xue. 2021;42(3):1569–1580. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

