Caspase-11 interaction with NLRP3 potentiates the noncanonical activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome
- PMID: 35487985
- PMCID: PMC9106893
- DOI: 10.1038/s41590-022-01192-4
Caspase-11 interaction with NLRP3 potentiates the noncanonical activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome
Abstract
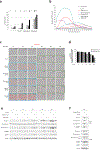
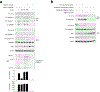
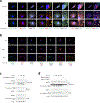
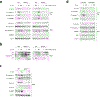
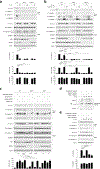
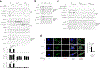
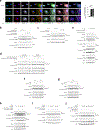
Caspase-11 detection of intracellular lipopolysaccharide (LPS) from invasive Gram-negative bacteria mediates noncanonical activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome. While avirulent bacteria do not invade the cytosol, their presence in tissues necessitates clearance and immune system mobilization. Despite sharing LPS, only live avirulent Gram-negative bacteria activate the NLRP3 inflammasome. Here, we found that bacterial mRNA, which signals bacterial viability, was required alongside LPS for noncanonical activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome in macrophages. Concurrent detection of bacterial RNA by NLRP3 and binding of LPS by pro-caspase-11 mediated a pro-caspase-11-NLRP3 interaction before caspase-11 activation and inflammasome assembly. LPS binding to pro-caspase-11 augmented bacterial mRNA-dependent assembly of the NLRP3 inflammasome, while bacterial viability and an assembled NLRP3 inflammasome were necessary for activation of LPS-bound pro-caspase-11. Thus, the pro-caspase-11-NLRP3 interaction nucleated a scaffold for their interdependent activation explaining their functional reciprocal exclusivity. Our findings inform new vaccine adjuvant combinations and sepsis therapy.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature America, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
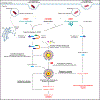

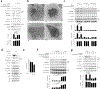
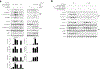
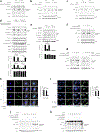

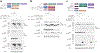
Comment in
-
Dual ligand engagement for noncanonical inflammasome activation.Nat Immunol. 2022 May;23(5):651-653. doi: 10.1038/s41590-022-01188-0. Nat Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35487984 No abstract available.
References
-
- Kayagaki N et al. Noncanonical inflammasome activation by intracellular LPS independent of TLR4. Science 341, 1246–1249 (2013). - PubMed
-
- Shi J et al. Inflammatory caspases are innate immune receptors for intracellular LPS. Nature 514, 187–192 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Broz P & Dixit VM Inflammasomes: mechanism of assembly, regulation and signalling. Nat Rev Immunol 16, 407–420 (2016). - PubMed
-
- Broz P, Pelegrin P & Shao F The gasdermins, a protein family executing cell death and inflammation. Nat Rev Immunol 20, 143–157 (2020). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

