The association between diabetes coexisting with low levels of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol and peritoneal dialysis-related peritonitis
- PMID: 35488249
- PMCID: PMC9052536
- DOI: 10.1186/s13098-022-00832-x
The association between diabetes coexisting with low levels of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol and peritoneal dialysis-related peritonitis
Abstract
Background: Low levels of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) and diabetes are common in patients undergoing peritoneal dialysis (PD). The aim of this study was to investigate the association between the coexistence of diabetes with a low level of HDL-C and the first episode of peritoneal dialysis-related peritonitis (PDRP) in patients with PD.
Methods: We retrospectively investigated patients with PD from January 1, 2003, to May 31, 2020, in four PD centers. Patients with PD were divided into four groups: no comorbidities, low HDL-C only, diabetes only, and diabetes plus low HDL-C. The clinical and laboratory baseline data of the four groups were collected and compared. The association between diabetes coexisting with low HDL-C levels and the first episode of PDRP was analyzed by multivariate Cox regression analysis.
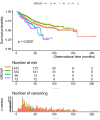
Results: A total of 1013 patients with PD were included in our study. The mean age was 49.94 ± 14.32 years, and 597 (58.99%) patients were males. A total of 301 (29.7%) patients had their first episodes of PDRP, and low HDL-C levels coexisted with diabetes in 72 patients with PD. After adjusting for confounding factors, a low level of HDL-C coexisting with diabetes was significantly associated with the first episode of PDRP in our study (hazard ratio: 2.81, 95% CI 1.32 ~ 4.73, p = 0.005). The associations among HDL-C, diabetes and PDRP were consistent in the following subgroups: sex, age, and pre-existing CVD (all P interaction > 0.05).
Conclusions: Patients with both diabetes and low HDL-C levels were at higher risk for PDRP in patients with PD.
Keywords: Diabetes; High-density lipoprotein cholesterol; Infection; Peritoneal dialysis; Peritonitis.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Perl J, Fuller DS, Bieber BA, Boudville N, Kanjanabuch T, Ito Y, Nessim SJ, Piraino BM, Pisoni RL, Robinson BM, Schaubel DE, Schreiber MJ, Teitelbaum I, Woodrow G, Zhao J, Johnson DW. Peritoneal dialysis-related infection rates and outcomes: results from the peritoneal dialysis outcomes and practice patterns study (PDOPPS) Am J Kidney Dis. 2020;76:42–53. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2019.09.016. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources