Comprehensive role of SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein in regulating host signaling pathway
- PMID: 35488404
- PMCID: PMC9348444
- DOI: 10.1002/jmv.27820
Comprehensive role of SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein in regulating host signaling pathway
Abstract
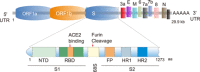
Since the outbreak of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection, global public health and the economy have suffered unprecedented damage. Based on the increasing related literature, the characteristics and pathogenic mechanisms of the virus, and epidemiological and clinical features of the disease are being rapidly discovered. The spike glycoprotein (S protein), as a key antigen of SARS-CoV-2 for developing vaccines, antibodies, and drug targets, has been shown to play an important role in viral entry, tissue tropism, and pathogenesis. In this review, we summarize the molecular mechanisms of interaction between S protein and host factors, especially receptor-mediated viral modulation of host signaling pathways, and highlight the progression of potential therapeutic targets, prophylactic and therapeutic agents for prevention and treatment of SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Keywords: ACE2 receptor; S protein; SARS-CoV-2; signaling pathway.
© 2022 Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

