"Fight-flight-or-freeze" - how Yarrowia lipolytica responds to stress at molecular level?
- PMID: 35488934
- PMCID: PMC9151528
- DOI: 10.1007/s00253-022-11934-x
"Fight-flight-or-freeze" - how Yarrowia lipolytica responds to stress at molecular level?
Abstract
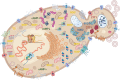
Yarrowia lipolytica is a popular yeast species employed in multiple biotechnological production processes. High resistance to extreme environmental conditions or metabolic burden triggered by synthetically forced over-synthesis of a target metabolite has its practical consequences. The proud status of an "industrial workhorse" that Y. lipolytica has gained is directly related to such a quality of this species. With the increasing amount of knowledge coming from detailed functional studies and comprehensive omics analyses, it is now possible to start painting the landscape of the molecular background behind stress response and adaptation in Y. lipolytica. This review summarizes the current state-of-art of a global effort in revealing how Y. lipolytica responds to both environmental threats and the intrinsic burden caused by the overproduction of recombinant secretory proteins at the molecular level. Detailed lists of genes, proteins, molecules, and biological processes deregulated upon exposure to external stress factors or affected by over-synthesis of heterologous proteins are provided. Specificities and universalities of Y. lipolytica cellular response to different extrinsic and intrinsic threats are highlighted. KEY POINTS: • Y. lipolytica as an industrial workhorse is subjected to multiple stress factors. • Cellular responses together with involved genes, proteins, and molecules are reviewed. • Native stress response mechanisms are studied and inspire engineering strategies.
Keywords: Environmental stress; Heterologous protein; Metabolic burden; Recombinant protein secretion; Stress response; Yeast.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Ewelina Celińska declares that she has no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Andreishcheva EN, Isakova EP, Sidorov NN, Abramova NB, Ushakova NA, Shaposhnikov GL, Soares MIM, Zvyagilskaya RA. Adaptation to salt stress in a salt-tolerant strain of the yeast Yarrowia lipolytica. Biochem. 1999;64:1061–1067. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

