Lifestyle and metabolic factors for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Mendelian randomization study
- PMID: 35488966
- PMCID: PMC9329390
- DOI: 10.1007/s10654-022-00868-3
Lifestyle and metabolic factors for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Mendelian randomization study
Abstract
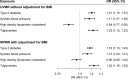
The risk factors for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) have not been clearly identified. We conducted a Mendelian randomization (MR) study to explore this. Independent genetic variants strongly associated with 5 lifestyle and 9 metabolic factors were selected as instrumental variables from corresponding genome-wide association studies (GWASs). Summary-level data for NAFLD were obtained from a GWAS meta-analysis of 8434 cases and 770,180 non-cases (discovery dataset) and another GWAS meta-analysis of 1483 cases and 17,781 non-cases (replication dataset). Univariable and multivariable MR analyses were performed. There were associations with NAFLD for lifetime smoking index (odds ratio (OR) 1.59, 95% confidence interval (CI) 1.31-1.93 per SD-increase), body mass index (BMI, OR 1.33, 95% CI 1.23-1.43 per SD-increase), waist circumference (OR 1.82; 95% CI 1.48-2.24 per SD-increase), type 2 diabetes (OR 1.21, 95% CI 1.15-1.27 per unit increase in log-transformed odds), systolic blood pressure (OR 1.17; 95% CI 1.07-1.26 per 10 mmHg increase), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (OR 0.84, 95% CI 0.77-0.90 per SD-increase), and triglycerides (OR 1.23, 95% CI 1.15-1.33 per SD-increase). The associations for type 2 diabetes, systolic blood pressure, triglycerides, but not for high-density lipoprotein cholesterol remained strong after adjusting for genetically-predicted BMI. Genetic liability to type 2 diabetes mediated 51.4% (95% CI 13.4-89.3%) of the BMI-effects on NAFLD risk. There were suggestive inverse associations of genetically-predicted alcohol, coffee, and caffeine consumption, and vigorous physical activity with NAFLD risk. This study identified several lifestyle and metabolic factors that may be causally implicated in NAFLD.
Keywords: Lifestyle; Mendelian randomization; Metabolic factor; Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
DG is employed part-time by Novo Nordisk. All authors declare no support from any organization for the submitted work.
Figures
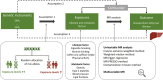

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

