F/YGG-motif is an intrinsically disordered nucleic-acid binding motif
- PMID: 35491929
- PMCID: PMC9067507
- DOI: 10.1080/15476286.2022.2066336
F/YGG-motif is an intrinsically disordered nucleic-acid binding motif
Abstract
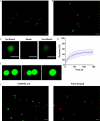
Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoproteins (hnRNP) function in RNA processing, have RNA-recognition motifs (RRMs) and intrinsically disordered, low-complexity domains (LCDs). While RRMs are drivers of RNA binding, there is only limited knowledge about the RNA interaction by the LCD of some hnRNPs. Here, we show that the LCD of hnRNPA2 interacts with RNA via an embedded Tyr/Gly-rich region which is a disordered RNA-binding motif. RNA binding is maintained upon mutating tyrosine residues to phenylalanines, but abrogated by mutating to alanines, thus we term the RNA-binding region 'F/YGG motif'. The F/YGG motif can bind a broad range of structured (e.g. tRNA) and disordered (e.g. polyA) RNAs, but not rRNA. As the F/YGG otif can also interact with DNA, we consider it a general nucleic acid-binding motif. hnRNPA2 LCD can form dense droplets, by liquid-liquid phase separation (LLPS). Their formation is inhibited by RNA binding, which is mitigated by salt and 1,6-hexanediol, suggesting that both electrostatic and hydrophobic interactions feature in the F/YGG motif. The D290V mutant also binds RNA, which interferes with both LLPS and aggregation thereof. We found homologous regions in a broad range of RNA- and DNA-binding proteins in the human proteome, suggesting that the F/YGG motif is a general nucleic acid-interaction motif.
Keywords: Liquid-liquid phase separation; disordered proteins; low complexity domain; nucleic acid interaction; sequence motif.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the authors.
Figures





References
-
- Gilbert W. Origin of life: the RNA world. Nature. 1986;319(618):86.
-
- Hentze MW, Castello A, Schwarzl T, et al. A brave new world of RNA-binding proteins. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2018;19(5):327–341. - PubMed
-
- Manning G, Whyte DB, Martinez R, et al. The protein kinase complement of the human genome. Science. 2002;298(5600):1912–1934. - PubMed
-
- Zheng N, Shabek N. Ubiquitin ligases: structure, function, and regulation. Annu Rev Biochem. 2017;86:129–157. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
