Multiple plaque incisions with or without grafting for Peyronie's disease
- PMID: 35492223
- PMCID: PMC9045568
- DOI: 10.1002/bco2.130
Multiple plaque incisions with or without grafting for Peyronie's disease
Abstract
Objectives: To assess novel surgical techniques in management of Peyronie's disease.
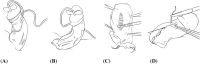
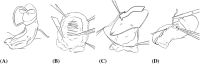
Subjects: Forty-three men underwent corrective surgery using either partial plaque incision and nongraft (PPING) or multiple plaque incisions and graft (MPIG). The technique used was determined intra-operatively. Patients were assessed at baseline and follow-up based on Peyronie's disease questionnaire patient-reported outcome measure (PDQ-PROM) and erectile function.
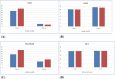
Results: The two groups were well matched in age and erectile function. At baseline MPIG group had greater deformity and poorer patient-reported outcome. Penile curvature improved from 67.9° to 10.5° in the PPING group and 77.9° to 7.1° with MPIG. PDQ-PROM improved from 29 to 13 in those who underwent PPING and 38.5 to 17.6 in those undergoing MPIG. Erectile function was preserved in both groups.
Conclusions: These novel surgeries are effective in restoring penile shape and length while preserving erectile function. This is reflected in improved patient-reported outcomes. These findings should be verified by multi-institutional study.
Keywords: IIEF; PROM; Peyronie's disease; incision; plaque.
© 2021 The Authors. BJUI Compass published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of BJU International Company.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
Comment in
-
Male and Female Sexual Function and Dysfunction; Andrology.J Urol. 2023 Jan;209(1):282-284. doi: 10.1097/JU.0000000000003019. Epub 2022 Oct 12. J Urol. 2023. PMID: 36250934 No abstract available.
References
-
- Weidner W, Hauck EW, Schnitker J. Potassium paraaminobenzoate (POTABA) in the treatment of Peyronie's disease: A prospective, placebo‐controlled, randomized study. Eur Urol. 2005;47:530–5. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
