Assessment of Reticulocyte and Erythrocyte Parameters From Automated Blood Counts in Vaso-Occlusive Crisis on Sickle Cell Disease
- PMID: 35492334
- PMCID: PMC9044919
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2022.858911
Assessment of Reticulocyte and Erythrocyte Parameters From Automated Blood Counts in Vaso-Occlusive Crisis on Sickle Cell Disease
Abstract
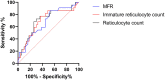
Sickle cell disease is a complex genetic disease involving cell adhesion between red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets and endothelial cells, inducing painful vaso-occlusive crisis (VOC). We assessed reticulocyte and erythrocyte parameters in a cohort of confirmed SCD patients, and investigated whether a combination of these routine laboratory biomarkers of haemolysis could be used to predict VOC development. Reticulocyte and erythrocyte parameters were evaluated using the Sysmex XN-9000 analyser. A total of 98 patients with SCD were included, 72 in steady state and 26 in VOC. Among the 72 patients in steady state, 22 developed a VOC in the following year (median: 3 months [2-6]). The following parameters were increased in SCD patients with VOC development compared to SCD patients without VOC development in the following year: reticulocyte count (94.6 109/L [67.8-128] vs. 48.4 109/L [24.9-87.5]), immature reticulocyte count (259 109/L [181-334] vs. 152 109/L [129-208]) reticulocyte/immature reticulocyte fraction (IRF) ratio (6.63 109/(L*%) [4.67-9.56] vs. 4.94 109/(L*%) [3.96-6.61]), and medium fluorescence reticulocytes (MFR) (19.9% [17.4-20.7] vs. 17.1% [15.95-19.75]). The association of a reticulocyte count of >189.4 109/L and an MFR of >19.75% showed a sensitivity of 81.8% and a specificity of 88% to predict VOC development in the following year. Based on our findings, a combination of routine laboratory biomarkers, as reticulocyte count, immature reticulocyte count and fluorescent reticulocyte fraction at steady state, could be used to predict VOC development in SCD.
Keywords: erythrocyte parameters; immature reticulocyte fraction; reticulocyte count; sickle cell disease; vaso-occlusive crisis.
Copyright © 2022 Feugray, Kasonga, Grall, Benhamou, Bobée-Schneider, Buchonnet, Daliphard, Le Cam Duchez, Lahary and Billoir.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Urbina A, Palomino F. In vitro kinetics of reticulocyte subtypes: maturation after red blood cell storage in additive solution-1 (AS-1). Hematol Transfus Cell Ther. (2018) 40:143–50. 10.1016/j.htct.2017.12.002 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

