Nanozyme-based catalytic theranostics
- PMID: 35492517
- PMCID: PMC9048033
- DOI: 10.1039/c9ra09021e
Nanozyme-based catalytic theranostics
Abstract
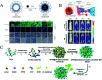
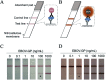
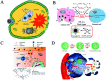
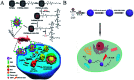
Nanozymes, a type of nanomaterial with intrinsic enzyme-like activities, have emerged as a promising tool for disease theranostics. As a type of artificial enzyme mimic, nanozymes can overcome the shortcomings of natural enzymes, including high cost, low stability, and difficulty in storage when they are used in disease diagnosis. Moreover, the multi-enzymatic activity of nanozymes can regulate the level of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in various cells. For example, superoxide dismutase (SOD) and catalase (CAT) activity can be used to scavenge ROS, and peroxidase (POD) and oxidase (OXD) activity can be used to generate ROS. In this review, we summarize recent progress on the strategies and applications of nanozyme-based disease theranostics. In addition, we address the opportunities and challenges of nanozyme-based catalytic theranostics in the near future.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Wang X. Hu Y. Wei H. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2016;3:41–60. doi: 10.1039/C5QI00240K. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

