Journey of anthraquinones as anticancer agents - a systematic review of recent literature
- PMID: 35492773
- PMCID: PMC9043427
- DOI: 10.1039/d1ra05686g
Journey of anthraquinones as anticancer agents - a systematic review of recent literature
Abstract
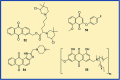
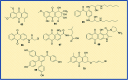
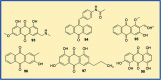
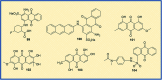
Anthraquinones are privileged chemical scaffolds that have been used for centuries in various therapeutic applications. The anthraquinone moiety forms the core of various anticancer agents. However, the emergence of drug-resistant cancers warrants the development of new anticancer agents. The research endeavours towards new anthraquinone-based compounds are increasing rapidly in recent years. They are used as a core chemical template to achieve structural modifications, resulting in the development of new anthraquinone-based compounds as promising anticancer agents. Mechanistically, most of the anthraquinone-based compounds inhibit cancer progression by targeting essential cellular proteins. Herein, we review new anthraquinone analogues that have been developed in recent years as anticancer agents. This includes a systematic review of the recent literature (2005-2021) on anthraquinone-based compounds in cell-based models and key target proteins such as kinases, topoisomerases, telomerases, matrix metalloproteinases and G-quadruplexes involved in the viability of cancer cells. In addition to this, the developments in PEG-based delivery of anthraquinones and the toxicity aspects of anthraquinone derivatives are also discussed. The review dispenses a compact background knowledge to understanding anthraquinones for future research on the expansion of anticancer therapeutics.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures

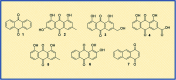


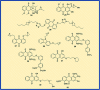
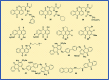
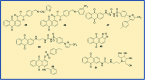





References
-
- Tian W. Wang C. Li D. Hou H. Future Med. Chem. 2020;12:627–644. - PubMed
-
- Demselben Justus Liebigs Ann. Chem. 1840;34:287–296. doi: 10.1002/jlac.18400340305. - DOI
-
- Graebe C. Ber. Dtsch. Chem. Ges. 1890;23:3739–3740. doi: 10.1002/cber.189002302361. - DOI
-
- Phillips M. Chem. Rev. 1929;6:157–174. doi: 10.1021/cr60021a007. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

