Optimization of bacterial cytokine protein production by response surface methodology for environmental bioremediation
- PMID: 35492803
- PMCID: PMC9043431
- DOI: 10.1039/d1ra03565g
Optimization of bacterial cytokine protein production by response surface methodology for environmental bioremediation
Abstract
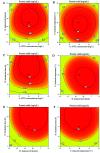
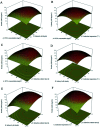
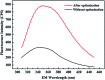
In natural and engineered systems, most microorganisms would enter a state of dormancy termed as "viable but non-culturable" (VBNC) state when they are exposed to unpredictable environmental stress. One of the major advances in resuscitating from such a state is the discovery of a kind of bacterial cytokine protein called resuscitation-promoting factor (Rpf), which is secreted from Micrococcus luteus. In this study, the optimization of Rpf production was investigated by the response surface methodology (RSM). Results showed that an empirical quadratic model well predicted the Rpf yield, and the highest Rpf protein yield could be obtained at the optimal conditions of 59.56 mg L-1 IPTG, cell density 0.69, induction temperature 20.82 °C and culture time 7.72 h. Importantly, Phyre2 web portal characterized the structure of the Rpf domain to have a shared homology with lysozymes, and the highest lysozyme activity was at pH 5 and 50 °C. This study broadens the knowledge of Rpf production and provided potential strategies to apply Rpf as a bioactivator for environmental bioremediation.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures



References
-
- Ma R. Yan X. Mi X. Wu Y. Qian J. Zhang Q. Chen G.-H. Chem. Eng. J. 2021;425:131457. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2021.131457. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

