High and Rapid Increase in Seroprevalence for SARS-CoV-2 in Conakry, Guinea: Results From 3 Successive Cross-Sectional Surveys (ANRS COV16-ARIACOV)
- PMID: 35493112
- PMCID: PMC8992319
- DOI: 10.1093/ofid/ofac152
High and Rapid Increase in Seroprevalence for SARS-CoV-2 in Conakry, Guinea: Results From 3 Successive Cross-Sectional Surveys (ANRS COV16-ARIACOV)
Abstract
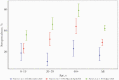
We conducted 3 successive seroprevalence surveys, 3 months apart, using multistage cluster sampling to measure the extent and dynamics of the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 epidemic in Conakry, the capital city of Guinea. Seroprevalence increased from 17.3% (95% CI, 12.4%-23.8%) in December 2020 during the first survey (S1) to 28.9% (95% CI, 25.6%-32.4%) in March/April 2021 (S2), then to 42.4% (95% CI, 39.5%-45.3%) in June 2021 (S3). This significant overall trend of increasing seroprevalence (P < .0001) was also significant in every age class, illustrating a sustained transmission within the whole community. These data may contribute to defining cost-effective response strategies.
Keywords: COVID-19; Guinea; SARS-CoV-2; population-based survey; seroprevalence.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Infectious Diseases Society of America.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization. WHO coronavirus (COVID-19) dashboard. Available at: https://covid19.who.int/. Accessed 25 January 2022.
-
- Massinga Loembe M, Tshangela A, Salyer SJ, et al. COVID-19 in Africa: the spread and response. Nat Med 2020; 26:999–1003. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization. Population-based age-stratified seroepidemiological investigation protocol for COVID-19 virus infection. 2020. Available at: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/WHO-2019-nCoV-Seroepidemiology-2.... Accessed 25 January 2022.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

