Research Trends and Most Influential Clinical Studies on Anti-PD1/PDL1 Immunotherapy for Cancers: A Bibliometric Analysis
- PMID: 35493449
- PMCID: PMC9044908
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.862084
Research Trends and Most Influential Clinical Studies on Anti-PD1/PDL1 Immunotherapy for Cancers: A Bibliometric Analysis
Abstract
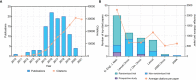
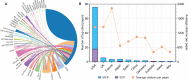
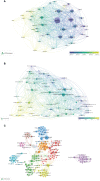
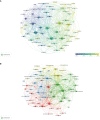
In this study, a bibliometric analysis was carried out to identify the most influential clinical studies and research trends on anti-programmed cell death 1/programmed cell death 1 ligand 1 (anti-PD1/PDL1) immunotherapy. On January 1, 2022, we used Web of Science to identify the 100 most frequently cited papers on clinical studies investigating anti-PD1/PDL1 immunotherapy, and extracted the following data: publication year, source title, country/region, institution, and the total number of citations. The research design and area were classified independently by the authors. Subsequently, we carried out a bibliometric analysis to determine the trends and identify the major journals on anti-PD1/PDL1 immunotherapy. The authors analyzed the current research hotspots based on papers published in major journals from 2020 to 2021. These 100 papers were cited a total of 138,840 times, and the median number of citations was 899.5 (range: 341-7,983). "Safety, activity, and immune correlates of anti-PD-1 antibody in cancer" by Topalian et al. had the highest number of citations (7,983 times). New England Journal of Medicine had the highest number of top-cited papers (40 papers), average citations per paper (1,558.3 citations), and rate of top-cited papers (65.6%). Authors from the USA contributed most of the papers (76 papers). Lung cancer (30 papers, 46,422 citations) and melanoma (20 papers, 30,881 citations) were the most cited research areas. In summary, anti-PD1/PDL1 has become standard treatment for various cancer, while adjuvant anti-PD1/PDL1 therapy is currently a research hotspot. New England Journal of Medicine was identified as the most influential journal in this area. Non-small cell lung cancer and melanoma are the most well-studied cancers, while nivolumab and pembrolizumab are the most commonly investigated anti-PD1/PDL1 antibodies. Further studies are warranted to identify effective predictive biomarkers or models, clarify the molecular mechanism of combined therapy, and establish optimal therapeutic strategies. This study may assist researchers in obtaining a comprehensive impression of the landscape and current trends in anti-PD1/PDL1 immunotherapy and gain inspiration to conduct further studies.
Keywords: PD1/PDL1; bibliometric analysis; clinical trials; immunotherapy; lung cancer; melanoma; tumor mutation burden.
Copyright © 2022 Liu, Xu, Cheng, Lin, Jiang, Yu, Zhang, Lu and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Pawelczyk K, Piotrowska A, Ciesielska U, Jablonska K, Gletzel-Plucinska N, Grzegrzolka J, et al. . Role of PD-L1 Expression in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer and Their Prognostic Significance According to Clinicopathological Factors and Diagnostic Markers. Int J Mol Sci (2019) 20:824. doi: 10.3390/ijms20040824 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wei SC, Duffy CR, Allison JP. Fundamental Mechanisms of Immune Checkpoint Blockade Therapy. Cancer Discov (2018) 8:1069–86. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-18-0367 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

