Weak Expression of Terminal Complement in Active Antibody-Mediated Rejection of the Kidney
- PMID: 35493506
- PMCID: PMC9044906
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.845301
Weak Expression of Terminal Complement in Active Antibody-Mediated Rejection of the Kidney
Abstract
Background: The role of the complement system in antibody-mediated rejection (ABMR) is insufficiently understood. We aimed to investigate the role of local and systemic complement activation in active (aABMR). We quantified complement activation markers, C3, C3d, and C5b-9 in plasma of aABMR, and acute T-cell mediated rejection (aTCMR), and non-rejection kidney transplant recipients. Intra-renal complement markers were analyzed as C4d, C3d, C5b-9, and CD59 deposition. We examined in vitro complement activation and CD59 expression on renal endothelial cells upon incubation with human leukocyte antigen antibodies.
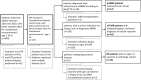
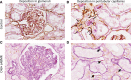
Methods: We included 50 kidney transplant recipients, who we histopathologically classified as aABMR (n=17), aTCMR (n=18), and non-rejection patients (n=15).
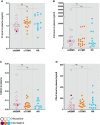
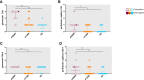
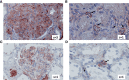
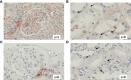
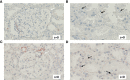
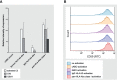
Results: Complement activation in plasma did not differ across groups. C3d and C4d deposition were discriminative for aABMR diagnosis. Particularly, C3d deposition was stronger in glomerular (P<0,01), and peritubular capillaries (P<0,05) comparing aABMR to aTCMR rejection and non-rejection biopsies. In contrast to C3d, C5b-9 was only mildly expressed across all groups. For C5b-9, no significant difference between aABMR and non-rejection biopsies regarding peritubular and glomerular C5b-9 deposition was evident. We replicated these findings in vitro using renal endothelial cells and found complement pathway activation with C4d and C3d, but without terminal C5b-9 deposition. Complement regulator CD59 was variably present in biopsies and constitutively expressed on renal endothelial cells in vitro.
Conclusion: Our results indicate that terminal complement might only play a minor role in late aABMR, possibly indicating the need to re-evaluate the applicability of terminal complement inhibitors as treatment for aABMR.
Keywords: C5b-9; antibody-mediated rejection; complement system; kidney transplantation; membrane-attack complex.
Copyright © 2022 Tiller, Lammerts, Karijosemito, Alkaff, Diepstra, Pol, Meter-Arkema, Seelen, van den Heuvel, Hepkema, Daha, van den Born and Berger.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pathological study on the relationship between C4d, CD59 and C5b-9 in acute renal allograft rejection.Clin Transplant. 2004;18 Suppl 11:18-23. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0012.2004.00242. Clin Transplant. 2004. PMID: 15191368
-
C3D deposition in peritubular capillaries indicates a variant of acute renal allograft rejection characterized by a worse clinical outcome.Transplantation. 2003 Jul 15;76(1):102-8. doi: 10.1097/01.TP.0000069040.16457.06. Transplantation. 2003. PMID: 12865794
-
Capillary deposition of complement C4d and C3d in pediatric renal allograft biopsies.Transplantation. 2005 May 27;79(10):1435-40. doi: 10.1097/01.tp.0000158420.26623.0f. Transplantation. 2005. PMID: 15912116
-
Endothelial transcripts uncover a previously unknown phenotype: C4d-negative antibody-mediated rejection.Curr Opin Organ Transplant. 2010 Feb;15(1):42-8. doi: 10.1097/MOT.0b013e3283352a50. Curr Opin Organ Transplant. 2010. PMID: 20009933 Review.
-
Detection of alloantibody-mediated complement activation: A diagnostic advance in monitoring kidney transplant rejection?Clin Biochem. 2016 Mar;49(4-5):394-403. doi: 10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2015.05.024. Epub 2015 Jun 26. Clin Biochem. 2016. PMID: 26118475 Review.
Cited by
-
The Diagnostic Significance of C3d Antigen in Kidney and Skin Histopathology - The Current State-Of-The-Art and Practical Examples.Physiol Res. 2023 Oct 27;72(S3):S225-S232. doi: 10.33549/physiolres.935175. Physiol Res. 2023. PMID: 37888966 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Complement Activation is More Pronounced in the Kidneys of Critically Ill Patients With COVID-19 Than in Those With Bacterial Sepsis.Kidney Int Rep. 2025 Apr 21;10(7):2284-2295. doi: 10.1016/j.ekir.2025.04.027. eCollection 2025 Jul. Kidney Int Rep. 2025. PMID: 40677312 Free PMC article.
-
Complement component C3 and C5b-9 deposition on hypoxia reperfused endothelial cells by non-HLA antibodies against RhoGDI2: A player involved in graft failure?HLA. 2023 Feb;101(2):103-114. doi: 10.1111/tan.14858. Epub 2022 Nov 1. HLA. 2023. PMID: 36266772 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Schinstock CA, Mannon RB, Budde K, Chong AS, Haas M, Knechtle S, et al. . Recommended Treatment for Antibody-Mediated Rejection After Kidney Transplantation: The 2019 Expert Consensus From the Transplantion Society Working Group. Transplantation (2020) 104(5):911–22. doi: 10.1097/TP.0000000000003095 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Haas M, Loupy A, Lefaucheur C, Roufosse C, Glotz D, Seron D, et al. . The Banff 2017 Kidney Meeting Report: Revised Diagnostic Criteria for Chronic Active T Cell–Mediated Rejection, Antibody-Mediated Rejection, and Prospects for Integrative Endpoints for Next-Generation Clinical Trials. Am J Transplant (2018) 18(2):293–307. doi: 10.1111/ajt.14625 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

