A Comparison of Environmental Impact of Various Silicas Using a Green Chemistry Evaluator
- PMID: 35493693
- PMCID: PMC9044506
- DOI: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.2c00519
A Comparison of Environmental Impact of Various Silicas Using a Green Chemistry Evaluator
Abstract
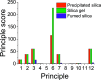
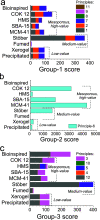
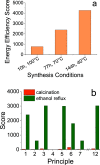
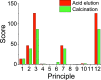
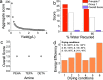
To answer questions surrounding the sustainability of silica production, MilliporeSigma's DOZN 2.0 Green Chemistry Evaluator was employed as it provides quantitative values based on the 12 principles of Green Chemistry. As a first study using DOZN 2.0 to evaluate the greenness of nanomaterials, a range of silica types were considered and their greenness scores compared. These included low- and high-value silicas, both commercial and emerging, such as precipitated, gel, fumed, colloidal, mesoporous, and bioinspired silicas. When surveying these different types of silicas, it became clear that while low value silicas have excellent greenness scores, high-value silicas perform poorly on this scale. This highlighted the tension between high-value silicas that are desired for emerging markets and the sustainability of their synthesis. The calculations were able to quantify the issues pertaining to the energy-intensive reactions and subsequent removal of soft templates for the sol-gel processes. The importance of avoiding problematic solvents during processes and particularly releasing them as waste was identified. The calculations were also able to compare the amount of waste generated as well as their hazardous nature. The effects of synthesis conditions on greenness scores were also investigated in order to better understand the relationship between the production process and their sustainability.
© 2022 American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures



References
-
- Meon W.; Blume A.; Luginsland H.-D.; Uhrlandt S.. Silica and Silanes. In Rubber Compounding: Chemistry and Applications; Rodgers B., Ed.; Marcel Dekker, Inc.: Akron, OH, 2004; pp 285–364.
-
- Aldhufairi H. S.; Olatunbosun O. A. Developments in tyre design for lower rolling resistance: A state of the art review. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part D: Journal of Automobile Engineering 2018, 232 (14), 1865–1882. 10.1177/0954407017727195. - DOI
-
- Roland R.Rubber compound and tires based on such a compound. EP 0501227A1, 1992.
-
- Slowing I. I.; Trewyn B. G.; Giri S.; Lin V. S. Y. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery and Biosensing Applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2007, 17 (8), 1225–1236. 10.1002/adfm.200601191. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
